Figure 2.
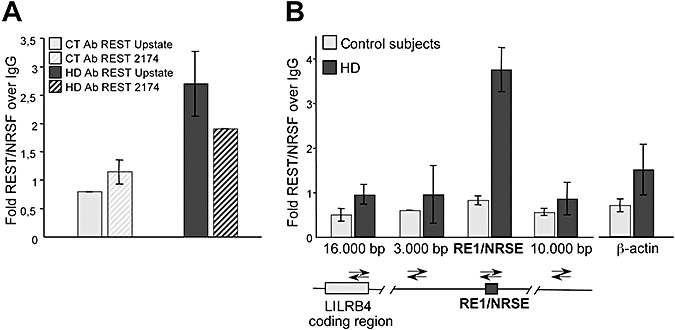
Repressor element‐1 silencing transcription factor/neuron‐restrictive silencer factor (REST/NRSF) chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) in human lymphocytes is specific. A. ChIP at the RE1/NRSE of the leukocyte immunoglobulin‐like receptor, subfamily B, member 4 (LILRB4) locus using two different anti‐REST/NRSF antibodies; the similar results confirm the specificity of the ChIP assay. In addition, repressor element‐1/neuron‐restrictive silencer element (RE1/NRSE) occupancy of the LILRB4 locus was greater in the patients with Huntington's disease (HD) than in the controls (CT). B. ChIP scanning of the LILRB4 locus. Quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction was performed on the precipitated DNA fragments using four pairs of oligonucleotide primers designed to produce amplicons covering the RE1/NRSE site in the LILRB4 gene and flanking sequences, located 16.000 bp, on coding region of LILRB4, and 3.000 bp upstream and 10.000 bp downstream of the RE1/NRSE. The scanning ChIP assay shows peak of REST/NRSF occupancy centered at the RE1/NRSE site of the LILRB4 gene. There is no enrichment in distal regions or in the coding region of LILRB4 and the β‐actin gene, which is not regulated by REST/NRSF. Abbreviations: IgG = immunoglobulin G.
