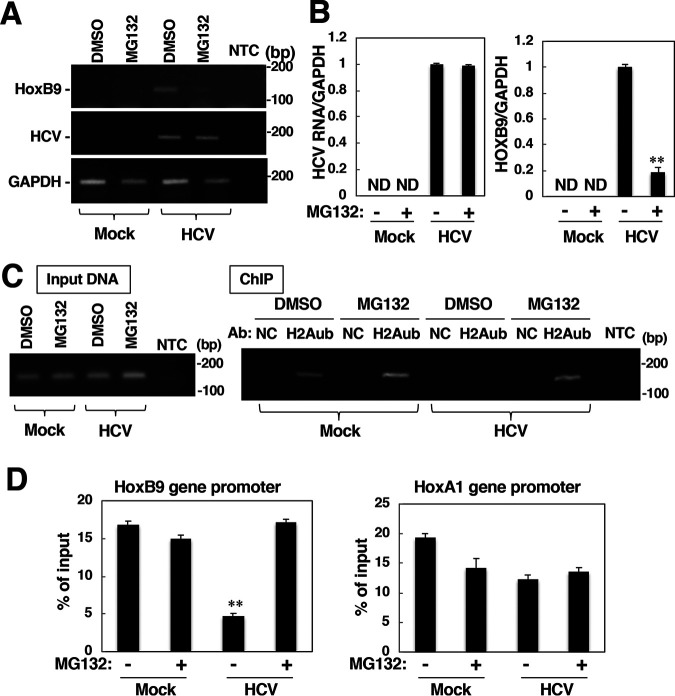
FIG 11.
Proteasome inhibitor treatment increased H2Aub in the HOXB9 gene promoter and suppressed HOXB9 transcription. Mock-infected cells and HCV-infected cells were treated with 10 μM MG-132 or DMSO and were then harvested 4 h after treatment. (A) Total RNA was prepared from those cells. The levels of HCV RNA, HOX9 mRNA and GAPDH mRNA were evaluated by RT-sqPCR. (B) The values were quantified by RT-qPCR using total RNA samples described in panel A. These levels of HCV RNA and HOX9 mRNA were normalized to the level of GAPDH mRNA. (C) Nuclear fractions were subjected to a ChIP assay using normal IgG (NC) or anti-H2Aub IgG (H2Aub). The level of H2Aub bound to the HOXB9 gene promoter was estimated based on the level of immunoprecipitated fragments originating from the HOXB9 gene promoter. The levels of the HOXB9 gene promoter in the total fraction (left panel, input DNA) and in the immunoprecipitated fraction (right panel, ChIP) from each group were estimated by sqPCR. (D) The level of H2Aub bound to the HOXB9 or HOXA1 gene promoter in each group was estimated by a ChIP assay. The data shown in this figure are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± SD values (n = 3). **, P < 0.01; ND, not detected.