FIG 12.
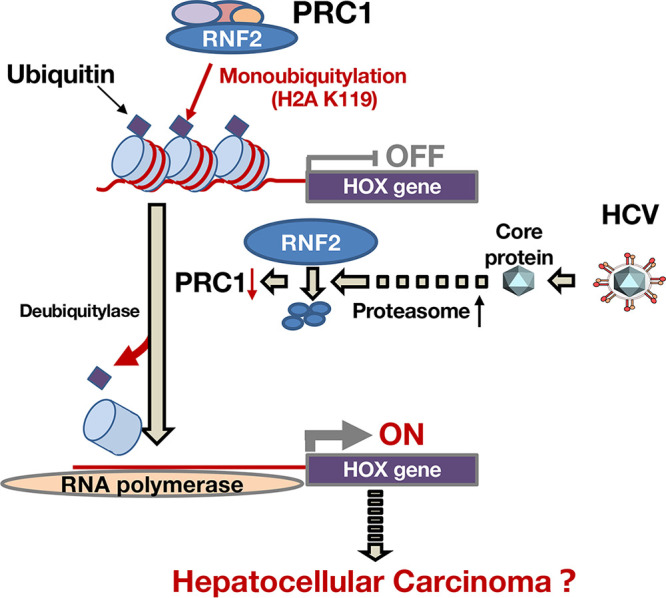
A schematic diagram of HOX gene induction in HCV-infected cells. The mechanism by which HCV infection induces expressions of HOX genes is summarized as a schematic diagram. PRC1 is known as a silencer of gene expression such as HOX gene expression. PRC1 monoubiquitinates histone H2A K119 as an E3 ubiquitin-ligase and then suppresses the transcription of the HOX gene in noninfected hepatocytes. HCV infects hepatocytes, and then the core protein is released into the cytosol. The core protein induces the activation of proteasome activity and the degradation of RNF2, which is a main component of PRC1. The degradation of RNF2 loses the balance between deubiquitylase and ubiquitin ligase with regard to H2A K119 monoubiquitination, leading to inductions of HOX genes. These findings may be a part of the mechanism associated with the hepatitis C-related disorders, including hepatocellular carcinoma.
