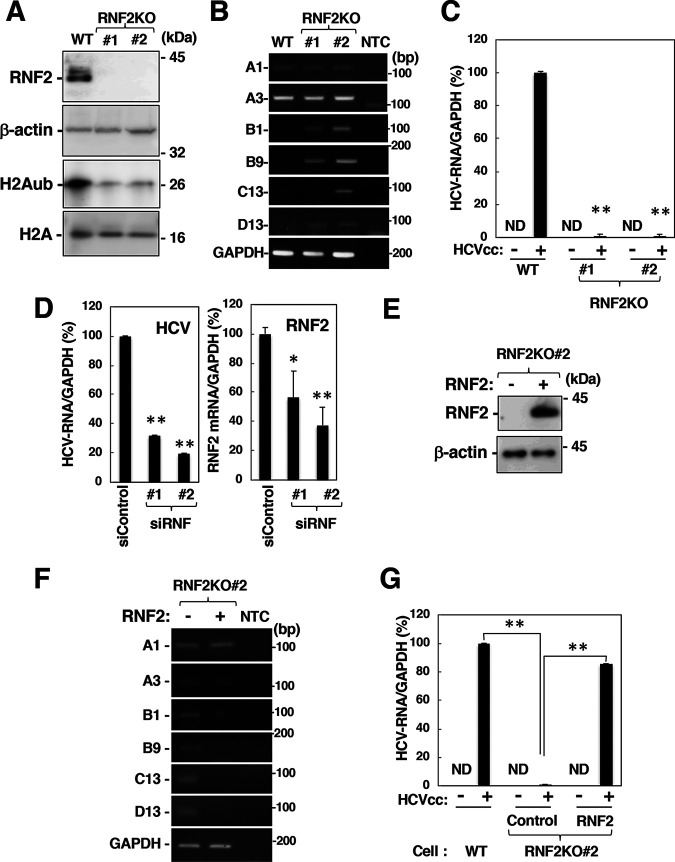
FIG 6.
Involvement of RNF2 in HOX gene induction and HCV propagation. (A) Cell lysates were prepared from the parental cell line (wild type [WT]) and the RNF2KO#1 and RNF2KO#2 cell lines and were then subjected to Western blotting. (B) The mRNA levels of HOXA1, HOXA3, HOXB1, HOXB9, HOXC13, HOXD13, and GAPDH in these cells were evaluated by RT-sqPCR. A1, A3, B1, B9, C13, and D13 indicate HOXA1, HOXA3, HOXB1, HOXB9, HOXC13, and HOXD13. (C) Parental, RNF2KO#1, and RNF2KO#2 cells were infected with HCVcc at an MOI of 0.1. HCV-infected cells and mock-infected cells were harvested at 6 dpi. Intracellular HCV RNA and GAPDH mRNA levels were estimated by RT-qPCR. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± SD values (n = 3). (D) Two siRNAs targeting RNF2 (siRNF#1 and #2) were added to a culture supernatant of Huh7OK1 cells at 10 nM. Transfected cells were infected with HCVcc at 24 h posttransfection. HCV-infected cells were harvested at 2 dpi. HCV RNA and GAPDH mRNA levels were evaluated by RT-qPCR. (E and F) A plasmid encoding RNF2 was transfected into RNF2KO#2 cells. The transfected cells were harvested at 36 h for preparation of total RNA and cell lysates. HOX gene mRNA levels were estimated by RT-sqPCR. RNF2 and β-actin expression was evaluated by immunoblotting (E) HOX gene mRNA levels were analyzed by RT-sqPCR. (F) A1, A3, B1, B9, C13, and D13 indicate HOXA1, HOXA3, HOXB1, HOXB9, HOXC13, and HOXD13. (G) A plasmid encoding RNF2 (RNF2) or an empty plasmid (Control) was transfected into RNF2KO#2 cells. The transfected cells were infected with HCVcc at an MOI of 0.1 at 36 h posttransfection. HCV-infected cells and mock-infected cells were harvested at 6 dpi. (C, D, and G) The data shown are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as the mean ± SD values (n = 3). **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; ND, not detected.