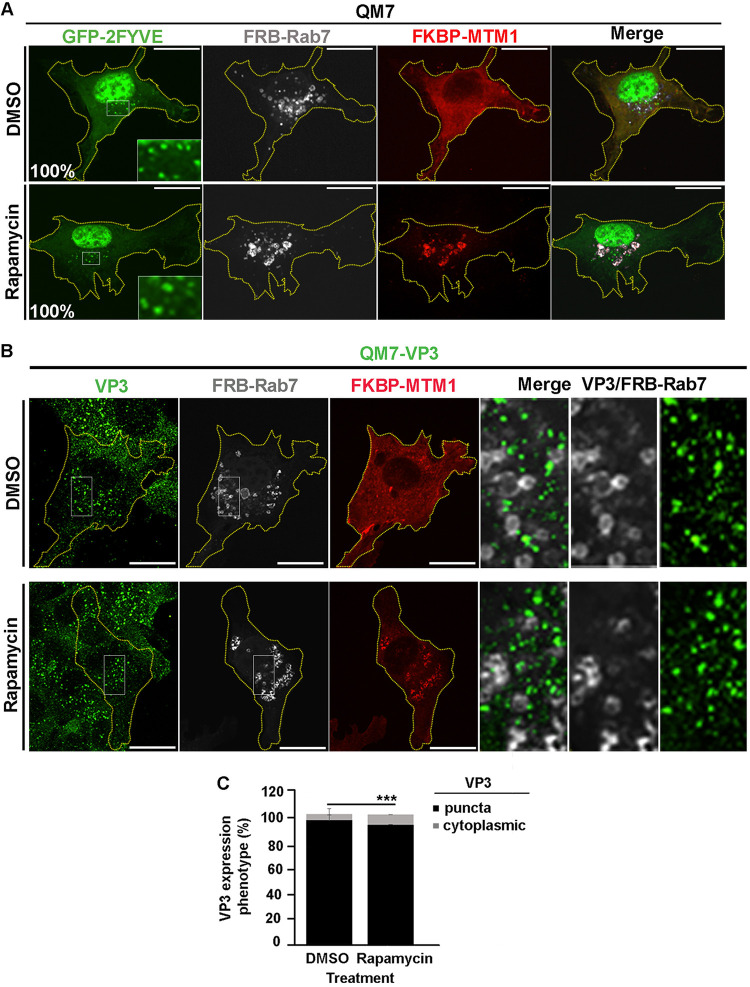
FIG 7.
The rapamycin-induced recruitment of MTM1 to Rab7-positive compartments does not prevent VP3-EE association. (A) Analysis of GFP-2FYVE subcellular distribution in QM7 cells after rapamycin-induced recruitment of MTM1 to late endosomes. QM7 cells were transiently cotransfected with mCherry-FKBP-MTM1, iRFP-FRB-Rab7, and GFP-2FYVE for 12 h and subsequently treated for 15 min with DMSO or 1 μM rapamycin, to induce the recruitment of FKBP-MTM1 to the FRB-Rab7-decorated membranes. Cells were fixed and visualized by spinning-disc confocal microscopy. Main panels show representative images of merged z-stacks. Insets show amplified images that depict the intracellular localization of GFP-2FYVE. The images are representative of three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm. Percentages were calculated by analyzing 50 cells per condition. (B and C) Analysis of VP3 subcellular distribution after recruitment of MTM1 to late endosomes. (B) QM7-VP3 cells were transiently cotransfected with mCherry-FKBP-MTM1 and iRFP-FRB-Rab7 for 12 h and subsequently treated for 15 min with DMSO or 1 μM rapamycin. The cells were fixed, permeabilized, VP3 (green) stained as described in Materials and Methods, and analyzed by spinning-disc confocal microscopy. Representative images of merged z-stacks are shown. The images are representative of three independent experiments. Bars, 10 μm. (C) VP3 expression phenotypes (punctate or cytoplasmic) were determined employing Volocity software and following the criteria described in Materials and Methods. Twenty-five cells per condition were scored for each experiment. The images are representative of three independent experiments. Data are means and SD. ***, P < 0.01.