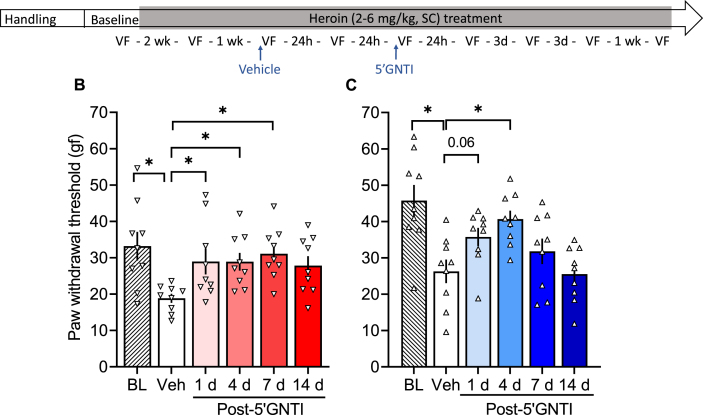
Fig. 4.
κ-Opioid receptor antagonist 5′GNTI reversed heroin withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia. (A) Male and female Wistar rats were handled and habituated to subcutaneous (SC) saline injections for 1 week before the baseline (BL) paw withdrawal threshold measure. All of the rats then received a subcutaneous heroin injection once per day, five times per week. After 2 weeks of heroin treatment, they were re-tested in the electronic von Frey test. On the following week, all of the rats received vehicle and were tested after 30 min (data shown in Figs. 6A) and 24 h (Veh). Next, all of the rats received a single injection of 5′GNTI (30 mg/kg, SC) and were tested at 30 min (data shown in Fig. 6A) and 1, 4, 7, and 14 days post-5′GNTI. Importantly, after their single 5′GNTI injection, the rats continued to receive their daily heroin treatment five times per week throughout the experiment. We tested hyperalgesia 4–6 h after heroin administration (i.e., acute withdrawal). (B) Female rats received vehicle, which was significantly different from the baseline measure, followed by 5′GNTI treatment. 5′GNTI reversed opioid withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia in females up to 7 days. (C) Male rats received vehicle, which was significantly different from the baseline measure, followed by 5′GNTI treatment. 5′GNTI reversed opioid withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia in males up to 4 days. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM and were analyzed using one-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test. *p < 0.05 different from Veh (n = 7–9/group). gf, gram force.