Figure 1.
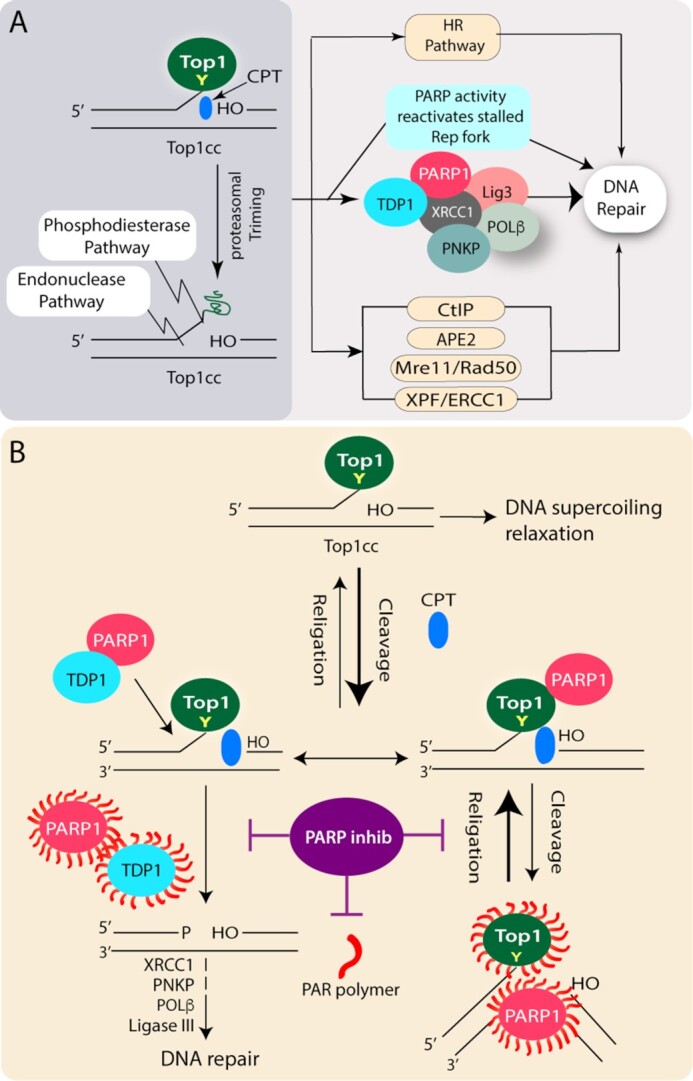
Induction of DNA damage with trapped Top1-DNA cleavage complexes (TOP1cc) and repair pathways. (A) Top1 cleaves one strand of duplex DNA via the nucleophilic attack of its active site tyrosine on the DNA phosphodiester backbone to yield a 3′-phosphotyrosyl bond. The short-lived covalent Top1-DNA cleavage complex (Top1cc) is readily trapped by Top1 poisons i.e. Camptothecin (CPT; blue) which binds in the interface of Top1-DNA complexes, stabilizes Top1cc, and inhibits the Top1-religation reaction. Scheme illustrating the repair pathways involved downstream to the proteasomal degradation of trapped Top1cc’s, which can be repaired in cells by broadly three pathways: (i) phosphodiesterase pathway: Excision of Top1 by TDP1 which is coupled with PARP1. PARP1 also reactivates stalled replication fork encountered by transient Top1cc; (ii) Endonuclease pathway: DNA cleavage by 3′-flap endonucleases such as XPF-ERCC1, Mre11/Rad50, CtIP and APE2; (iii) The Top1cc associated DSBs generated by replication run-off, results in a Top1-linked double-stranded end (DSE) which are repaired by homologous recombination repair. (B) PARP inhibitors the double-edged sword: Killing Top1 activity and inhibiting TDP1-mediated Top1cc repair. The short-lived covalent Top1-DNA cleavage complex (Top1cc) is readily reversed and facilitates DNA supercoil relaxation. The bold arrow indicates the shift in the cleavage/religation equilibrium in the presence of CPT (blue). PARylation of Top1 helps in the religation of the CPT-induced Top1 cleavage complex (Top1cc). While PARP coupling with TDP1 stimulates the excision of Top1cc by the phosphodiesterase activity of TDP1 and facilitates DNA repair. PARP inhibitors (purple) in combination with CPT abrogate Top1 and TDP1-PARylation, impair the repair of CPT-induced Top1cc, and promoting DSBs and cell death.
