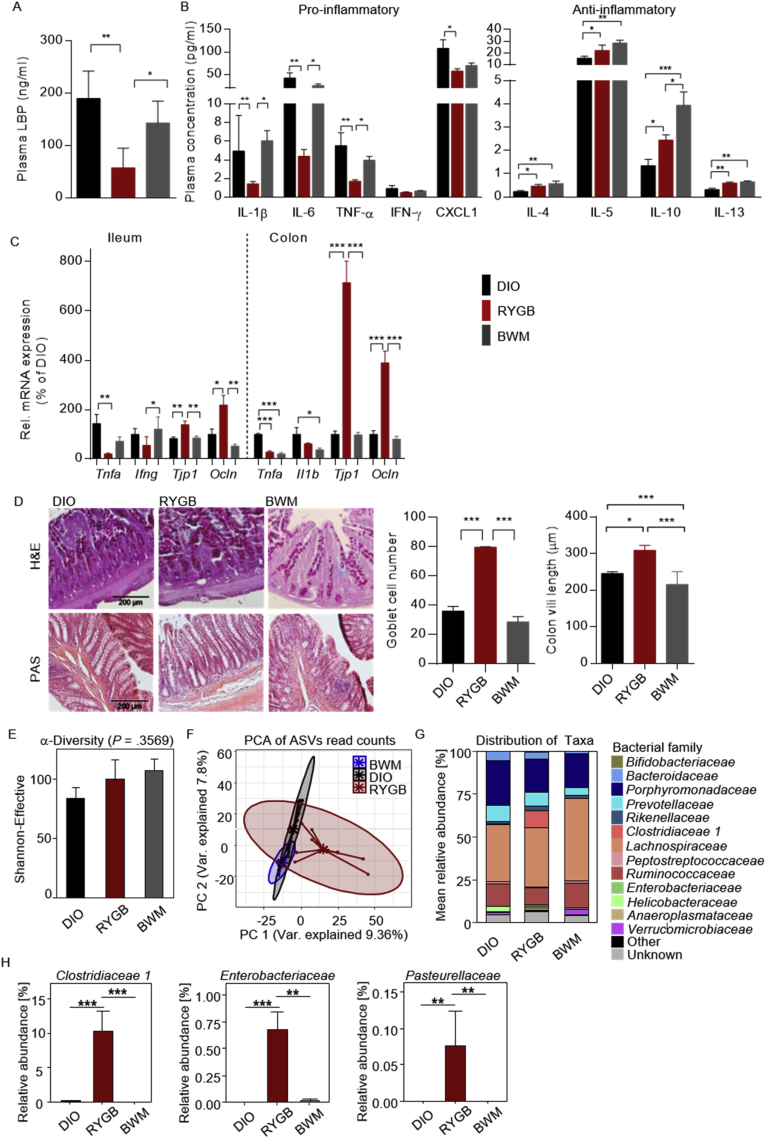
Figure 5.
Reduced LPS-binding protein and systemic pro-inflammatory tone was associated with a distinct shift in gut microbiota from RYGB surgery. (A) Plasma LPS-binding protein (LBP, ng/ml) levels at 12 weeks post-operatively. (B) Corresponding plasma pro- (IL-1β, IL6, TNF-α, INF-γ, and CXCL1) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, and IL13) cytokine levels. (C) Relative mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (Tnfa, Ifng, and Il1b) and markers of epithelial barrier integrity (Tjp1 and Ocln) in the ileum and colon of RYGB- and sham-operated DIO and BWM rats at 12 weeks post-operatively. (D) H&E and PAS staining of colon sections (scale bars, 200 μm) and morphometric quantification of villi length and goblet cell count per crypt. (E) Alpha diversity analysis profiles based on a principal component analysis (PCA) of 16S rRNA gene profiling data from cecal content collected from animals at 12 weeks post-operatively. (F) Beta diversity of microbiome (pairwise PERMANOVA, DIO vs RYGB = 0.001, DIO vs BWM = 0.011, and RYGB vs BWM = 0.001). (G) Mean abundance of bacterial families. (H) Significantly altered taxa between study groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–6 for A-D, n = 6–9 for E–H) with individual datapoints, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 for the effect of any indicated comparison.