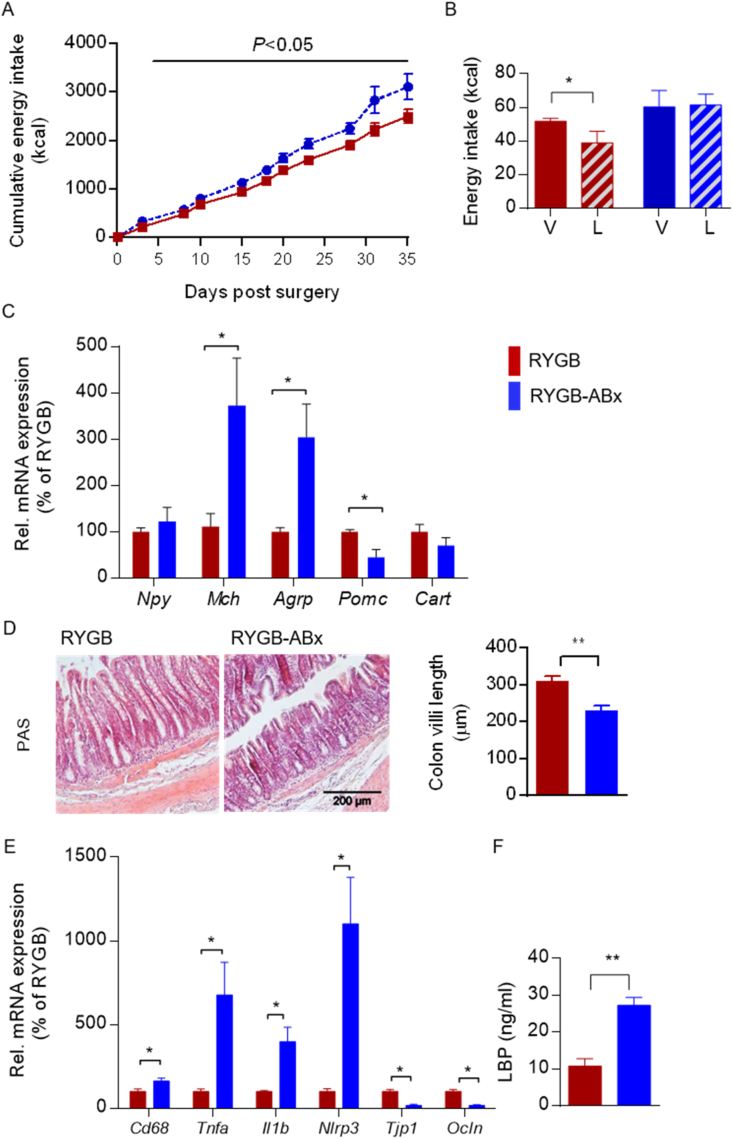
Figure 6.
RYGB surgery regulated hypothalamic feeding suppression and leptin's anorexigenic action in a gut microbiota-dependent manner. (A–F) RYGB-operated DIO rats at 5 weeks post-operatively were administered antibiotics (ABx) via drinking water for 5 weeks (RYGB-ABx). (A) Cumulative energy intake (kcal) after ABx (RYGB-ABx) vs control (RYGB) over a 35-day period (n = 9–11). (B) At 4 weeks after starting ABx, the animals received a single dose of leptin (i.p., 1 mg/kg, L) or vehicle (V) before 24-h energy intake (kcal) was recorded (n = 6). (C) Hypothalamic mRNA expression of Npy, Mch, Agrp, Pomc, and Cart (n = 4–6). (D) H&E staining of colonic sections (scale bar, 200 μm) and morphometric quantification of villi lengths (n = 3). (E) Relative mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory (Cd68, Tnfa, Il1b, and Nlrp3) and epithelial barrier integrity markers (Tjp1 and occludin) in the colon of RYGB- vs RYGB-ABx-treated DIO rats (n = 3–6). (F) Plasma LPS-BP (ng/ml) levels (n = 3–6). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–11 as indicated) with individual datapoints. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 for the effect of leptin-vs vehicle-injected animals (B) and RYGB- vs RYGB-ABx-treated DIO rats (C–E).