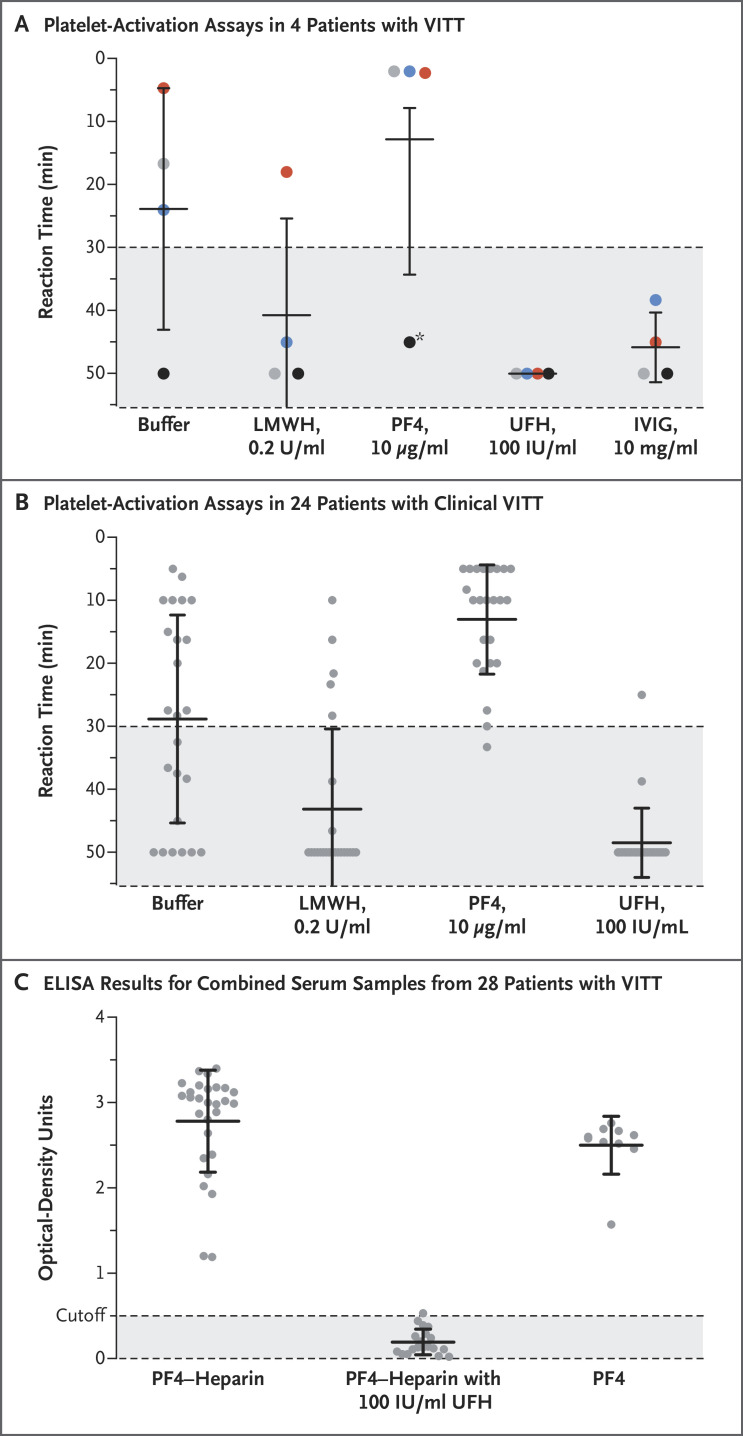
Figure 1. Reactivity of Patient Serum on Platelet-Activation Assays and Immunoassays.
Panel A shows the results of platelet-activation assays in serum samples obtained from the first 4 patients with vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) who were assessed in the study. The four colors in each experiment indicate the results obtained in the four samples; values are expressed as means, with 𝙸 bars indicating standard errors. The platelet-activation assay is performed by adding 20 μl of patient serum to 75 μl of washed platelets per well of a microtiter plate that contains the other reagents as indicated. Reactivity is expressed semiquantitatively as reaction time, with a shorter reaction time indicating stronger platelet-activating levels. A reaction time of more than 30 minutes indicates background or clinically insignificant reactivity. The asterisk indicates the reactivity of the outlier serum, which was strongly positive on subsequent retesting along with platelets of other volunteers in the presence of platelet factor 4 (PF4). Panel B shows the results of platelet-activation assays in serum samples obtained from an additional 24 patients with clinical VITT. The reactivity pattern resembles that observed in the 4 patients who were initially investigated. The serum caused variable platelet activation in the presence of buffer, which for most samples was inhibited in the presence of low-molecular-weight heparin but was strongly enhanced in the presence of PF4; in contrast, high levels of unfractionated heparin inhibited the reaction in all but one serum sample. Panel C shows the results of PF4–heparin and PF4 immunoassays of serum obtained from patients with VITT (including all 28 samples represented in Panels A and B) that showed PF4-dependent platelet activation. The results, which were obtained with the use of a microplate reader with a 450-nm filter, include all 28 PF4–heparin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) experiments (with the addition of 100 IU per milliliter of heparin in 19 experiments) and the results of 10 PF4 ELISA experiments. The cutoff for a negative result is 0.50 optical-density units. LMWH denotes low-molecular-weight heparin, UFH unfractionated heparin, and IVIG intravenous immune globulin.