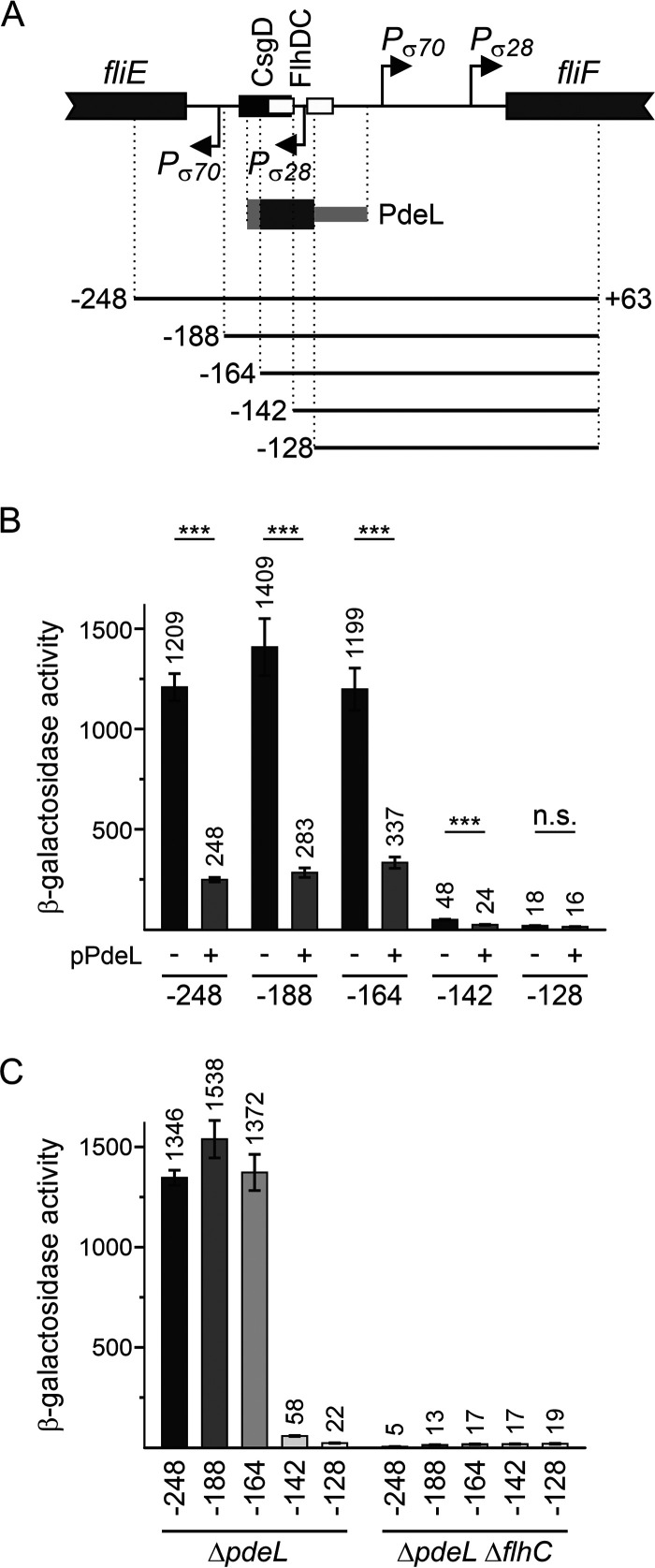
FIG 4.
The PdeL DNA-binding site overlaps the FlhD4C2 DNA-binding site. (A) Schematic of the PfliF region as shown in Fig. 3. Fragments “−248” to “−128,” depicted as solid lines, represent a deletion series of PfliF lacZ reporters carried on low-copy-number plasmids (pSC derivatives) (Table 2). The presumptive location of the PdeL DNA-binding site is indicated by a dark gray bar, while the light gray bar depicts the region of the PdeL DNA-binding site that was mapped by EMSAs (Fig. 3). The CsgD DNA-binding site maps at positions −178 to −145, and the FlhD4C2 DNA-binding sites map at positions −159 to −143 and −133 to −117 relative to the fliF translation start site. (B) The activity of the plasmidic PfliF lacZ reporters was tested in combination with plasmid pKECY44 carrying pdeL under the control of Para (+pPdeL) or plasmid pBAD30 as a control (−) in ΔlacZ ΔpdeL ΔaraBAD ΔaraFGH strain U290. Cultures for β-galactosidase assays were grown in tryptone medium with antibiotics. l-Arabinose was supplemented to a final concentration of 2 μM 1 h after inoculation. Cultures were harvested at an OD600 of 0.8 (after approximately 5 h of growth). Shown are mean values from four biological replicates, and error bars indicate standard deviations. Statistically significant differences are indicated with asterisks (***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant). (C) The activity of PfliF lacZ reporters was determined in transformants of ΔpdeL strain U266 and its ΔflhC derivative (U427). Cultures were grown similarly as described above for panel A but without the addition of arabinose. The differences in expression levels are all statistically significant except for PfliF lacZ at position −128.