Figure 5.
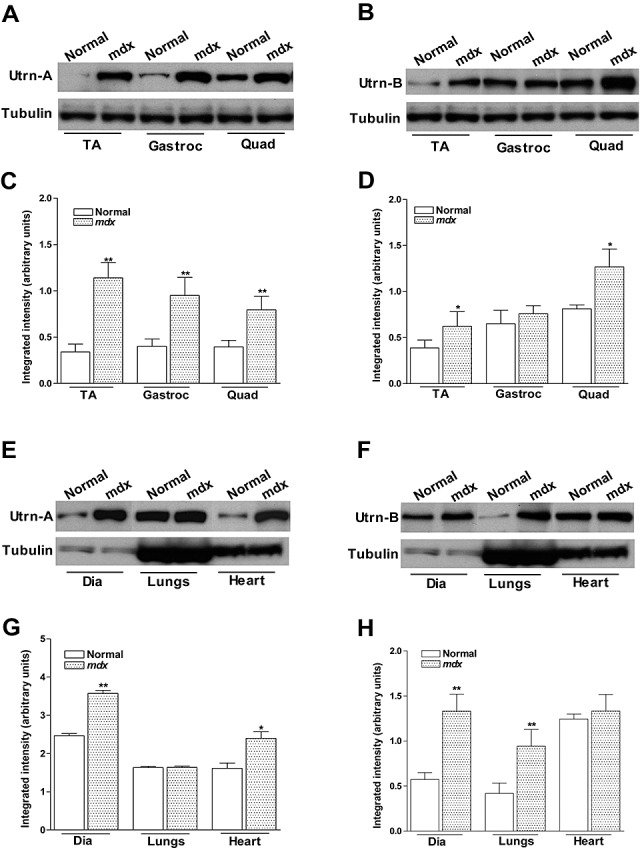
Quantitation of utrophin protein expression in normal and mdx mouse. Utrn‐A and Utrn‐B expression levels in normal and dystrophin‐deficient skeletal muscles (A–D), diaphragm, lungs and heart (E,H) were determined at translational level by immunoblotting. Western blot analysis of lysates containing 50 µg of total protein probed with Utrn‐A and ‐B antibodies. Utrn‐A protein was upregulated in mdx skeletal muscles, as shown (A,C). Quantification of Utrn‐A protein levels in normal and mdx muscles, expressed as normalized value of Utrn‐A/tubulin, revealed significant upregulation in tibialis anterior (TA), gastrocnemius (Gastroc) and quadriceps (Quad) muscles of mdx mice (C). Utrn‐B protein upregulation in the Gastroc was equivocal; however, tibialis anterior (TA) and Quad showed significantly higher expression than normal muscles (B). Lower lanes show blots probed with tubulin antibodies. Further, densitometric analysis confirmed significant upregulation of Utrn‐B in TA and Quad (D). Similarly, Utrn‐A and Utrn‐B expression levels in normal and mdx diaphragm (Dia), lungs and heart were determined at the translational levels (E–H). At the protein level, there was strong upregulation of Utrn‐A protein in mdx mouse Dia and heart, while in mouse lung, there was no upregulation of Utrn‐A as expected (E). Quantification of repeated blots of Utrn‐A, expressed as normalized value of Utrn‐A/tubulin, further confirmed significant upregulation of Utrn‐A in mdx Dia and heart (G). Among these tissues studied, Utrn‐B protein was significantly upregulated in lungs and diaphragm, but not in the heart (F). Densitometric analysis confirmed significant upregulation of Utrn‐B in Dia and lungs (H). Lower lanes show blots probed with tubulin antibodies. Histograms show means ± SD. Statistical analysis was conducted using Student's t‐tests. Each blot is a representative immunoblot from minimum of four experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.001.
