Figure 5.
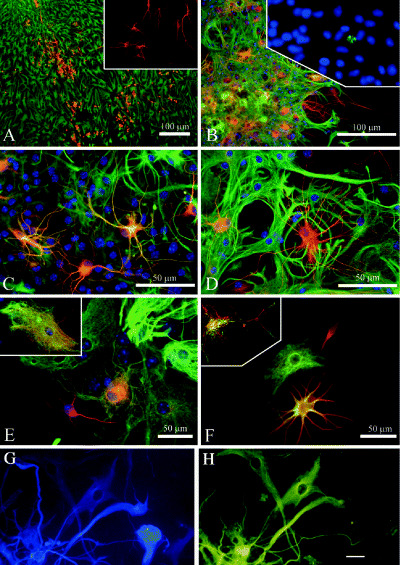
Examples of phenotypic fluidity in normal postnatal mouse astrocyte monolayer and neurosphere cultures, and in hybrid cells from adult human brain gliomas. Time‐dependent neuron/astrocyte hybrids in differentiating cerebellar spheres. A, and inset. Thirty‐six hours after attachment, spheres consist of separate populations of neurons (labeled for β‐III tubulin, red) and astrocytes [labeled for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), green]. B. Three days after attachment many yellow cells are seen which coexpress β‐III tubulin (red) and GFAP (green); inset in (B) caspase 3 immunolabeling (green) within a differentiating sphere at 72 h after attachment shows the fragmented nucleus of an apoptotic cell. Such labeling was rare, and most nuclei remained intact for extended in vitro periods. C and D. Higher magnification of neuron/astrocyte hybrids at 1 week post attachment show some cells expressing β‐III tubulin (red) and GFAP (green). Notice the hybrid morphology of thin, finely branched processes combined with stellate somata. Arrow in (D) indicates a coexpressing cell with two nuclei. E and F.β‐III tubulin and GFAP labeling reveals neuronal (red), astrocytic (green) and hybrid (yellow) phenotypes in adjacent cells. Inset in (E) is a high magnification of a cell with astrocytic morphology, showing β‐III tubulin (red) and GFAP (green) labeling of separate intracellular elements. Inset in (F) is a confocal micrograph of a single hybrid cell immunolabeled for β‐III tubulin (red) and GFAP (green) showing colocalization of these markers. G and H. Glioblastoma contain cells that under our culture conditions give rise to βIII tubulin+ neuron‐like cells (FITC), and cells that express the astroglial marker GFAP (blue, AMCA). In (G) there is a cell that is not labeled for GFAP, but is immunopositive for β‐III tubulin. Conversely, there are cells that are immunolabeled for GFAP, but immunonegative for β‐III tubulin, and a cell that is labeled with both immunomarkers (a so‐called “asteron”). Scale bars are 10 µm (G and H) and 100 µm (A–E). [From 38; copyright J Comp Neurol 2005, and 32; copyright Glia, 2002, with permission]
