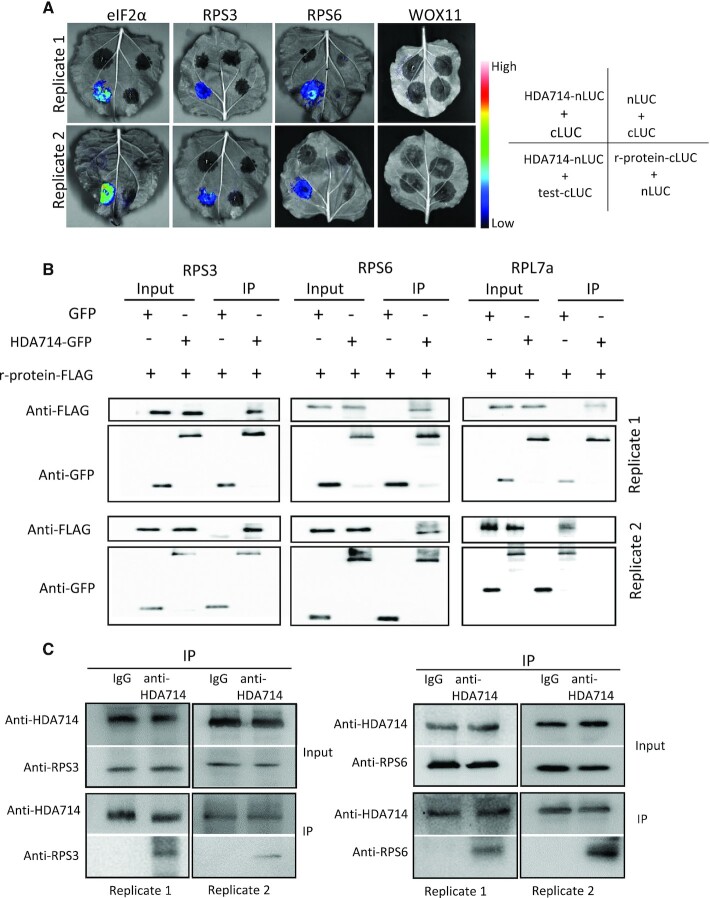
Figure 4.
In vivo protein interaction between HDA714 and ribosomal and IF proteins. (A) Tobacco leaves co-infiltrated with Agrobacterium containing 35S-driven split luciferase (LUC) constructs as indicated were photographed with a charge-coupled device camera. BiFC visualization showing that interaction between HDA714-Nluc and tested proteins (RPS16-cLUC, RPS3-cLUC, eIF2α-cLUC) in the N. benthamiana epidermal cells was observed. For the negative controls (nLUC + cLUC, HDA714-nLUC+cLUC, RPS6-cLUC+nLUC, RPS3-cLUC+nLUC, and eIF2α-cLUC+nLUC, HDA714-nLUC+WOX11-cLUC) no interaction was observed. eIF2α: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 alpha subunit. WOX11: WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX11 (WOX11) as a negative control. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation assay for the interaction between HDA714 and RPS3, RPS6 or RPL7a in vivo. Total proteins from N. benthamiana leaves co-expressing RPS3-, RPS6- or RPL7a-FLAG and HDA714-GFP were immunoprecipitated using anti-GFP agarose. The agarose-bound proteins were eluted and detected by immunoblotting using anti-GFP or anti-FLAG antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) Tests of in vivo interaction between HDA714 and RPS3 and RPS6 in rice plants. Proteins extracted from wild type rice plants were precipitated with IgG or anti-HDA714 and analyzed by immunoblots with anti-RPS3, anti-RPS6 and anti-HDA714. IP, immunoprecipitation.