Figure 4.
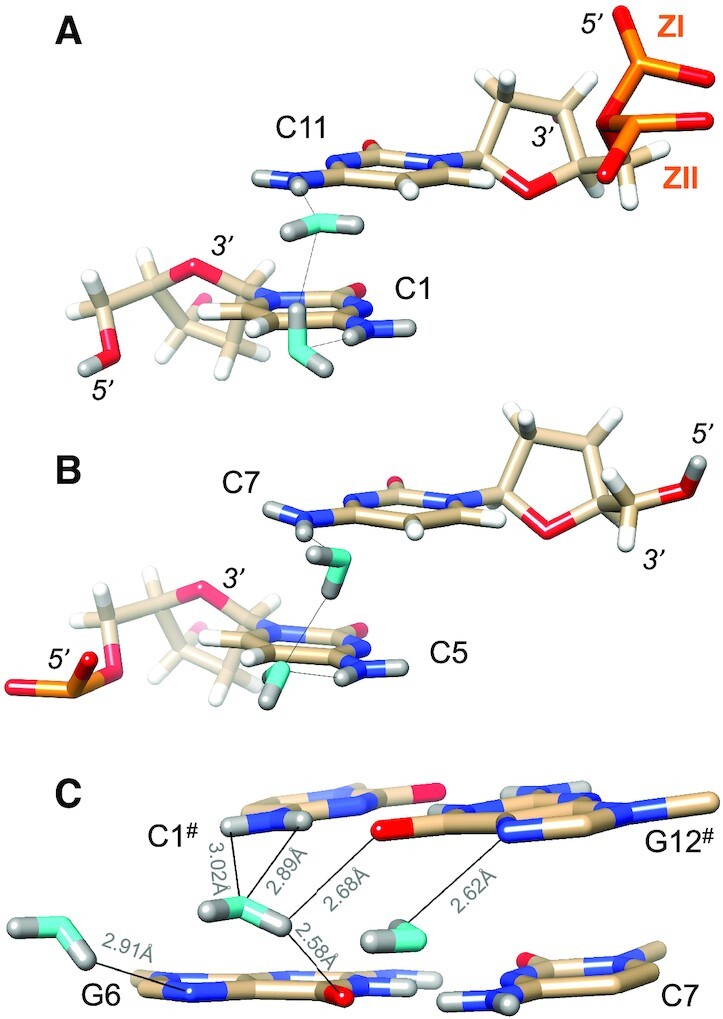
Water molecules bridging either pairs of cytosine N4 amino groups or pairs of guanine O6 keto groups on the convex surface. The Z-DNA neutron structure reveals H-bond donor-acceptor patterns for water bridges between cytosines (A) C1 and C11, and (B) C5 and C7. Water oxygen and deuterium atoms are colored in cyan and gray, respectively, and DNA deuterium and hydrogen atoms are colored in gray and white, respectively. H-bonds (D…O) are drawn as thin solid lines. (C) Water molecule bridging O6 keto oxygens of adjacent guanines on the convex surface (center), flanked by water molecules forming H-bonds to N7 of G6 and G12# (# marks a symmetry-related residue). Electrostatically favorable interactions by the central water are not limited to O6 (guanine) but also involve N4(C1#), i.e. a lone electron pair of water and the deuterium atoms of the amino group. D…N and D…O distances are indicated by thin solid lines.
