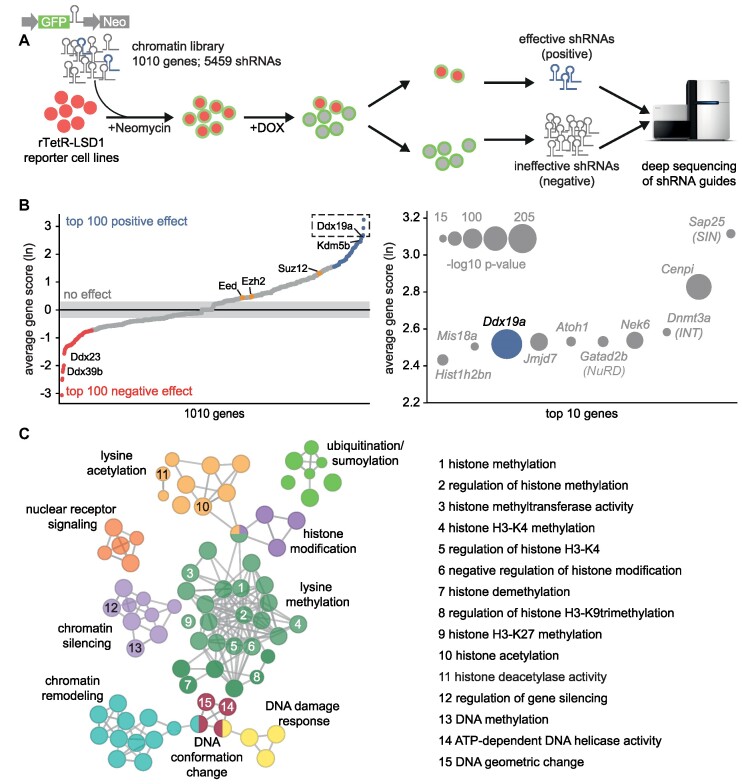
Figure 2.
A chromatin-focused shRNA screen identifies novel and known coregulators of LSD1 activity. (A) Workflow describing the ChECS screening strategy. A library composed of 5459 shRNAs targeting 1010 chromatin-related genes (GFP+) was virally transduced into rTetR-LSD1 reporter cell lines (mCherry+). After antibiotic selection, cells were treated with DOX for 14 days and FACS sorted for high (mCherry+) or low (mCherry-) mCherry expression. Genomic DNA was isolated from both populations and the shRNA guide sequences were amplified for Illumina sequencing. (B) Scatter plots ranking all genes according to their effect on LSD1 activity (gene score). Left: Gene scores of all genes present in the shRNA library. The gene score represents the Ln of the average enrichment score (read ratio mCherry+/mCherry-) of all shRNAs per gene across five replicates. Genes imposing a positive effect on LSD1 induced silencing are coloured in blue, genes having a negative effect are highlighted in red. The position of Ddx19a, Kdm5b and the PRC2 core components Suz12, Ezh2 and Eed is indicated. Right: Top ten genes identified in the screening procedure to positively influence LSD1 activity. Significance is represented by spot size (–log10P-value). (C) ClueGo network clustering the top 100 positive and negative regulators of LSD1 for their biological function (GO-annotated biological process). Biological processes of selected clusters are highlighted on the right. The statistical test used for the enrichment was based on a two-sided hypergeometric test with a Bonferroni correction and kappa score of 0.4. Only pathways with p≤0.01 are shown.