Figure 1.
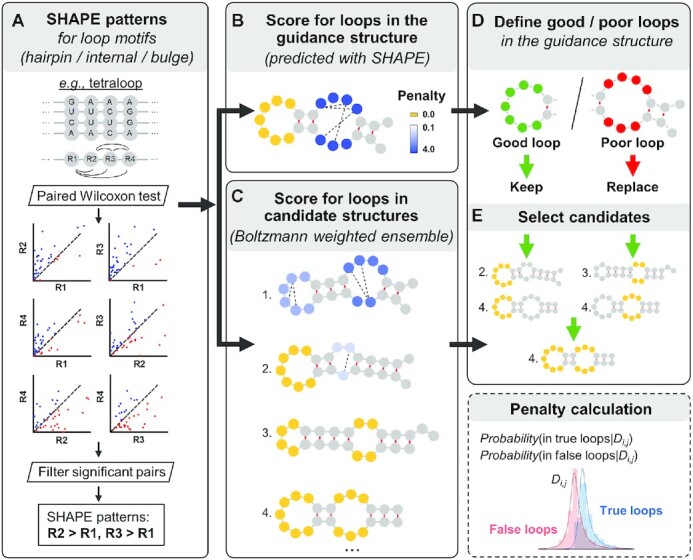
SHAPELoop workflow. (A) SHAPELoop is established based on the characteristic patterns of selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) for loop motifs of various types (hairpin, internal, and bulge) and lengths. The difference in SHAPE reactivities between any two positions of each loop motif is tested, and pairwise comparison results with sufficient significance are defined as the characteristic SHAPE patterns. The next two major steps of SHAPELoop are calculating penalties for loops in the guidance (minimum free energy, MFE) structure (B) and the Boltzmann-weighted candidate ensemble (C). Discrepancies between the SHAPE reactivities of predicted loops and the characteristic SHAPE patterns are estimated using a posterior probabilistic model and then used to calculate the penalties for predicted loops. (D) Loops in the guidance structure are divided into ‘good’ and ‘poor’ loops based on their penalties. (E) Candidates that retain all ‘good’ loops and have loops with lower penalties in ‘poor’ loop regions will be selected as the predicted structures.
