Figure 1.
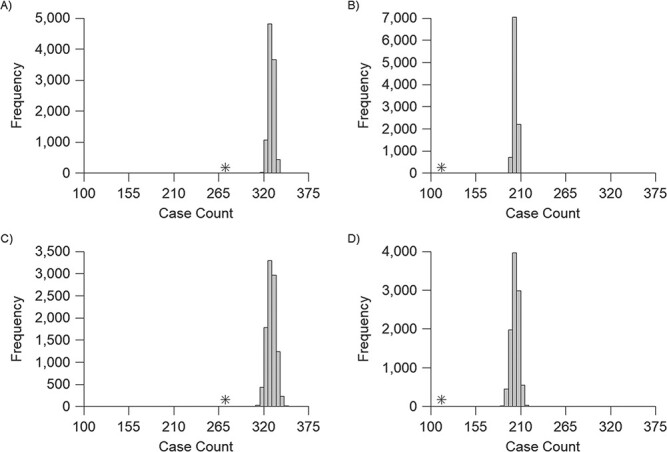
Comparison of infections defined using conventional and modified interpretations of paired serology among participants in a longitudinal cohort study conducted in Pau da Lima, Brazil, 2013--2015. In each panel, the case count using conventional interpretations of paired serology, which do not account for titer decay, is marked by an asterisk. Histograms show the number of infections defined in each of 10,000 imputations allowing for titer decay over all 6-month periods (A, C) or all 12-month periods (B, D). A and B use the point estimate of the decay rate, and C and D use a decay rate sampled from the distribution of the estimate.
