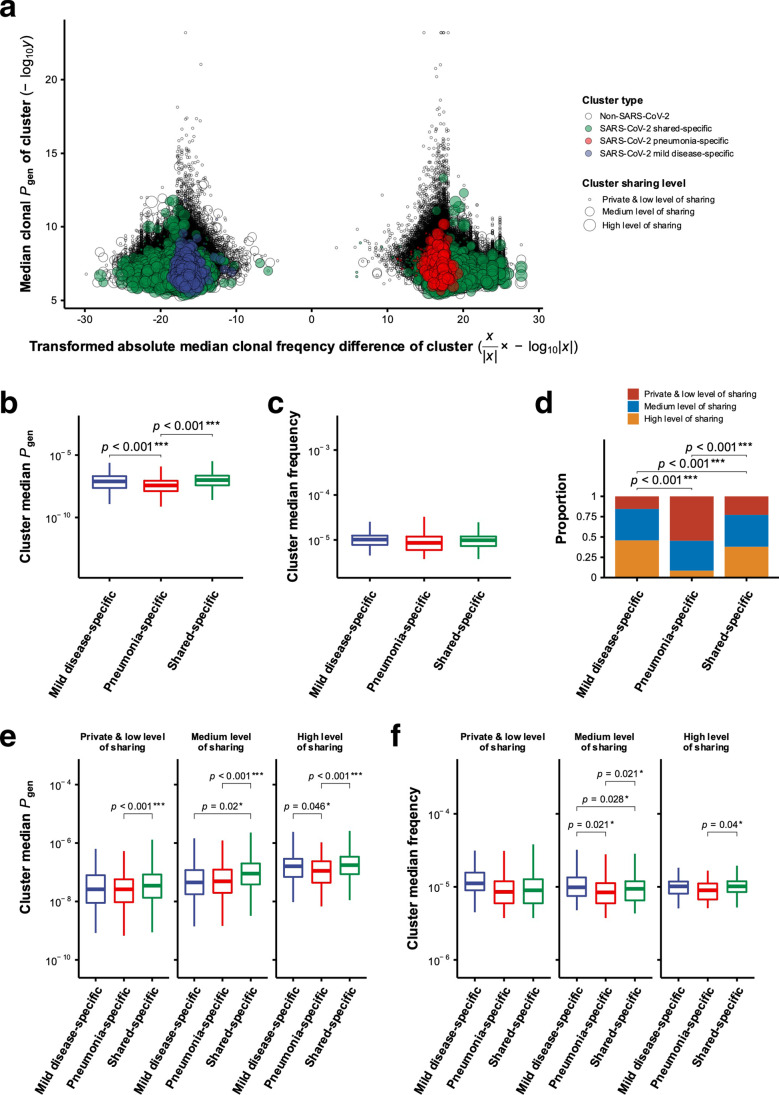
Fig. 3.
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2-associated TCRβ clusters enriched with TCRβ clonotypes from mild disease group, pneumonia group, and both groups of patients. a The distribution of transformed absolute difference of cluster median TCRβ frequencies (x-axis) and cluster median TCRβ generation probabilities (Pgen) (y-axis) of GLIPH2-identifying clusters was shown. Each circle represented one TCRβ cluster. The color and size of circles represented different patient-specific types and levels of sharing for TCRβ clusters, respectively. Only mild disease-, pneumonia-, and shared-specific TCRβ clusters with potential SARS-CoV-2 specificities were colored by blue, red, and green, respectively. The sharing level was denoted by private and low level of sharing, medium level of sharing, and high level of sharing. The value X for x-axis represented the absolute difference between median frequencies of clustered clonotypes contributed from pneumonia and mild disease groups of patients for each cluster. The value Y for y-axis indicated the median generation probability of all clonotypes within each cluster. b, c Comparison of cluster median Pgen and frequencies between SARS-CoV-2-associated mild disease- and pneumonia- and shared-specific TCRβ clusters was performed. Two-sided p values were shown from t-test. d Proportions of private and low level of sharing, medium level of sharing, and high level of sharing were compared between SARS-CoV-2-associated mild disease- and pneumonia- and shared-specific TCRβ clusters. p Values were shown from chi-square test. e, f Comparison of cluster median Pgen and frequencies between SARS-CoV-2-associated mild disease- and pneumonia- and shared-specific clusters, grouped by private and low level of sharing, medium level of sharing, and high level of sharing, was performed. Two-sided p values were shown from t-test. p Values larger than 0.05 were considered to be not statistically significant and were not shown