Fig. 3.
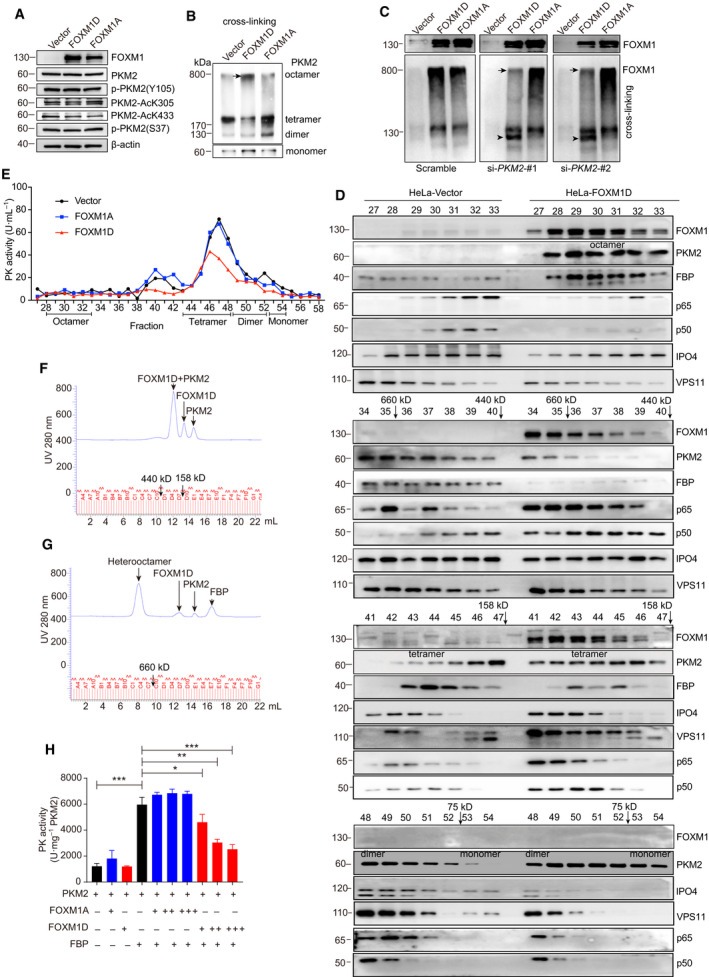
Tetrameric PKM2 assembles a heterooctamer with FOXM1D, thus reducing PK activity. (A) The phosphorylation and acetylation levels of PKM2 in HeLa cells with ectopic expression of FOXM1A/D. (B) Immunoassays detected that ectopic FOXM1D, but not FOXM1A, induced the emergence of a macromolecular protein complex (black arrow) containing PKM2 in cross‐linked samples from HeLa cells, thus altering the composition of PKM2 monomer and polymers. (C) The effect of PKM2 insufficiency on the formation of the FOXM1D and PKM2 complex. Up panel: the ectopic expression of FOXM1A/D using regular samples. Bottom panel: PKM2 insufficiency by specific siRNAs using cross‐linking samples reduced the FOXM1D‐containing (black arrow), but not the FOXM1A‐containing complex, leading to a new FOXM1 band (arrowhead). (D) Identification of the potential complex of FOXM1D and PKM2 in HeLa cells with ectopic expression of FOXM1D by gel chromatography and immunoblotting. FOXM1D assembles a heterooctamer with PKM2, predicted by the molecular weight. The fraction numbers, elution of molecular weight markers with arrows, and PKM2 monomer/polymers are indicated. (E) The PK activity of individual fractions from HeLa cells that were ectopic expression with vector, FOXM1A, or FOXM1D. (F) and (G) Identification of the interaction between FOXM1D and PKM2 in the absence (F) and presence (G) of FBP by gel chromatography. The three purified proteins were loaded in equal amounts (60 μg). (H) The measurement of PK activity in the different indicated mixtures. Each ‘+’ represents 10 μg of protein; thus, 10 μg of FOXM1/10 μg PKM2, 20 μg FOXM1/10 μg PKM2, and 30 μg FOXM1/10 μg PKM2 are about 0.665, 1.33, and 2, respectively, in molar ration. The data are analyzed by Student's t‐test (two‐tailed) and presented as mean ± SD; n = 3. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; and ****P < 0.0001 vs. control.
