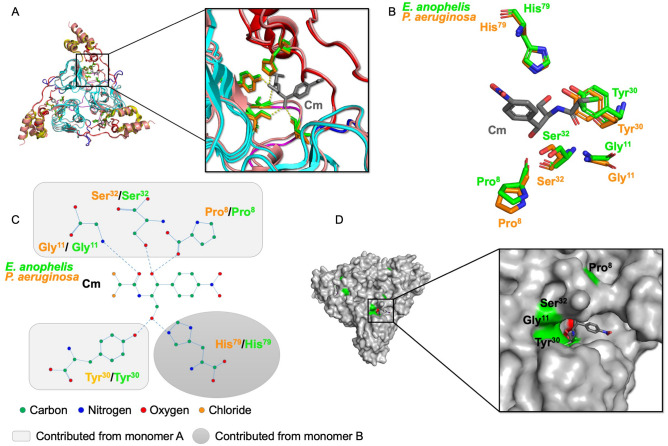
Figure 3.
Comparison of the Cm acceptor sites from E. anophelis CatB and P. aeruginosa catB7. (A) Superimposed structure of E. anophelis CatB (PDB ID: 6MFK) and P. aeruginosa catB7 (PDB ID: 2XAT29) trimer. Zoomed view to show H-bonding interactions between putative active site residues and Cm. (B) Cm binding site residues of E. anophelis and P. aeruginosa CAT proteins. Cm is shown in gray sticks. (C) Diagram of hydrogen bonds between residues of the E. anophelis and P. aeruginosa CAT proteins and Cm molecule. (D) E. anopheles CatB putative Cm acceptor site cavity. Cm is in gray sticks and residues important for H-bonding are coloured in green. Cm was modeled from the P. aeruginosa 2XAT29 structure.