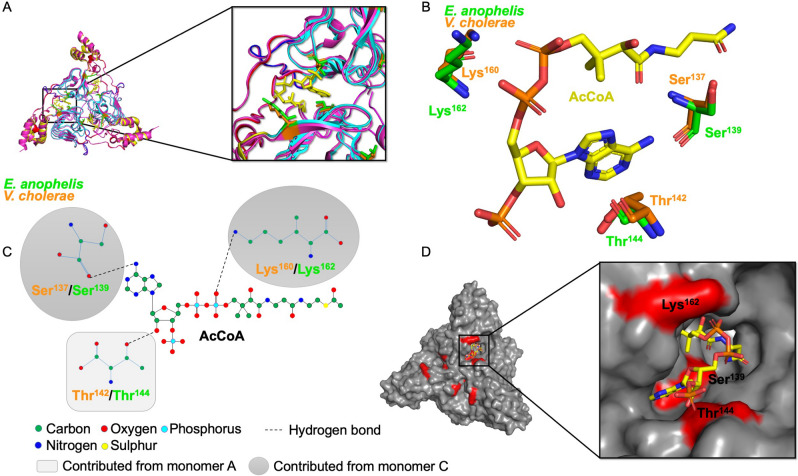
Figure 4.
Comparison of the AcCoA donor sites of E. anophelis CatB and V. cholerae catB7 proteins. (A) Superimposed structure of E. anophelis CatB (6MFK) and V. cholerae catB9 (6U9C27) trimer. Zoomed view to show residues surrounding AcCoA, shown in yellow sticks. (B) Putative active site residues of E. anophelis and V. cholerae CAT proteins found within the AcCoA binding site. (C) Diagram of hydrogen bonds between putative active site residues of the E. anophelis and V. cholerae CAT proteins and AcCoA molecule. (D) CatB putative active site cavity where AcCoA binds; residues important for H-bonding are coloured in red. AcCoA is in yellow sticks and is modeled from the V. cholerae 6U9C27 structure.