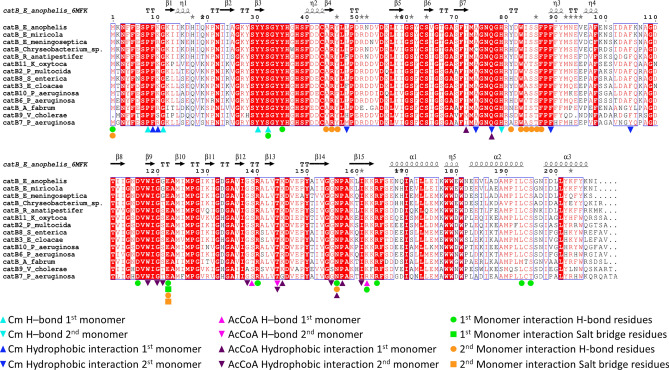
Figure 5.
Multiple sequence alignment of E. anophelis NUHP1 CAT with various Type B CATs from Flavobacteriaceae and validated Cm resistance proteins. The secondary structural elements of the E. anophelis NUHP1 protein (PDB ID: 6MFK) are shown above the multiple sequence alignment. Conserved residues are highlighted in red. Residues of the Cm binding site are denoted with cyan (H-bonds) and blue (hydrophobic interactions) symbols, where residues from one monomer are indicated with triangles and residues of the second monomer are shown as inverted triangles. Residues of the AcCoA binding site are denoted with magenta (H-bonds) and purple (hydrophobic) symbols, where residues from one monomer are indicated with triangles and residues of the second monomer are shown as inverted triangles. Green and orange symbols indicate interfacial residues that form H-bonds or salt bridges between protomers. Protein sequences within the alignment include: Elizabethkingia anophelis catB (UniProt ID A0A077EJ45), Elizabethkingia miricola catB (NCBI Accession KGO08276), Elizabethkingia meningoseptica catB (NCBI Accession QDZ61149), Chryseobacterium sp. catB (UniProt ID A0A3DMIM7), Riemerella anatipestifer catB (UniProt ID E5D2K4), Klebsiella oxytoca KONIH1 catB11 (NCBI Accession AID93387), Pasterurella multocida catB2 (UniProt ID Q83ZX9), Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi catB8 (UniProt ID Q79PD0), Enterobacter cloacae catB3 (UniProt ID C1IUN4), Pseudomonas aeruginosa catB10 (UniProt ID A2Q6I9), Pseudomonas aeruginosa catB6 (UniProt ID Q9R818), Agrobacterium fabrum str. C58 catB (UniProt ID P23364), Vibrio cholerae catB9 (UniProt ID H9L3X9), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 catB7 (UniProt ID P26841). The multiple sequence alignment was generated with ESpript (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/ESPript/).