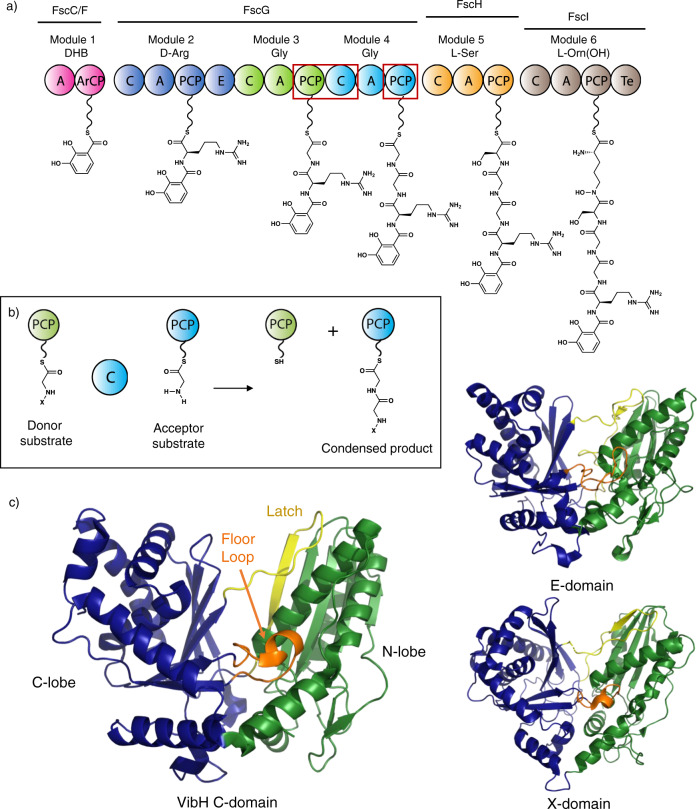
Fig. 1. Non-ribosomal peptide biosynthesis and structures of C-type domains.
a Scheme representing the biosynthesis of a linear precursor of fuscachelin A; the domains structurally characterized in this manuscript are indicated by red boxes. b Condensation domains catalyze peptide bond formation most commonly between thioester intermediates bound to adjacent PCP domains; for mechanistic discussion see Supplementary Information. c Left: crystal structure of an archetypal C-domain (VibH from vibriobactin biosynthesis, PDB ID: 1A); Top right: crystal structure of an epimerization domain from tyrocidine biosynthesis (PDB ID: 2G); Bottom right: crystal structure of the cytochrome P450 recruitment (X)-domain from teicoplanin biosynthesis (PDB ID: 42). These domains are all comprised of a V-shaped pseudo-dimer of chloramphenicol acetyl transferase (CAT) domains (colored green and blue), with crossover regions including the latch (lemon yellow) and floor loop (orange). A - adenylation domain, DHB - 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, ArCP - acyl carrier protein, C - condensation domain, E - epimerization domain, PCP - peptidyl carrier protein, Te - thioesterase domain, PPant moieties shown as undulated lines.