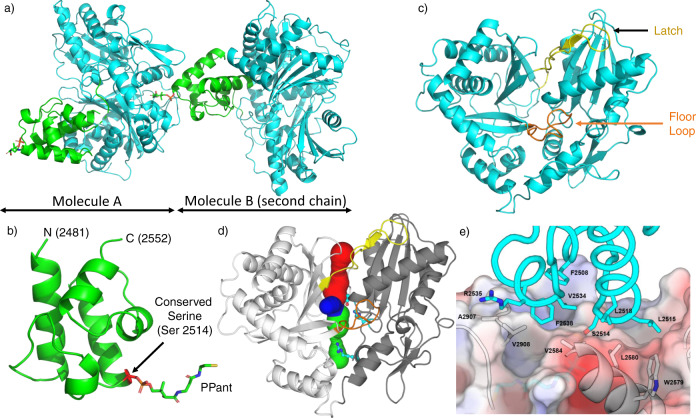
Fig. 2. Overview of the structure of the PCP2-C3 didomain from fuscachelin biosynthesis.
a Crystal structure of the PCP2-C3 didomain (PDB ID 7KVW) showing two chains, with the PCP domain positioned at the acceptor site of the C domain from another molecule (C domain shown in cyan, PCP shown in green). b Structure of the PCP2 domain, a 4-helix bundle with an additional small α-turn between helices 1 and 2 with the PPant arm bound to Ser2514. c Structure of the C3 domain, displaying a pseudo-dimer of CAT domains (latch and floor loop regions represented in yellow and orange, respectively); the donor binding site is at the top of the figure and the binding acceptor site is at the bottom of the figure. d C3 domain showing the donor tunnel (blue), acceptor tunnel (green), and a third tunnel (red) converging on the active site (blue). The tunnel lining residue R2577 and the active site residues E2702 and H2697 are shown as cyan sticks. e The hydrophobic interface between the PCP2 domain (cyan sticks and ribbon) and C3 domain (surface representation + gray sticks and ribbon). N - N-terminal, C - C-terminal, PPant - phosphopantetheinyl.