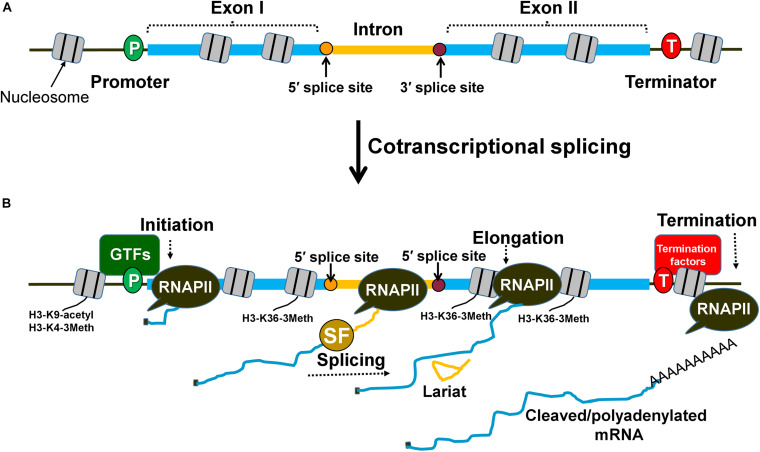
FIGURE 1.
Splicing occurs cotranscriptionally and affects different steps of transcription. (A) An intron within the transcribed region is flanked by exon I and exon II. The splice sites are designated as 5′ splice site and 3′ splice site and are the sites for spliceosome assembly during transcription. (B) Splicing factors are recruited cotranscriptionally to the intron with the help of the RNAPII carboxy-terminal domain. Spliceosomal assembly on the splice sites can facilitate the stabilization of general transcription factors (GTFs) at the promoter region of the gene and prime nucleosomes with activation marks (H3-K9 acetylation and H3-K4 trimethylation) for initiation. The splicing factors can also interact with transcription elongation factors and influence nucleosome modifications (H3-K36 trimethylation) to promote elongation. Similarly, splicing factors can contribute to enhanced termination of transcription by facilitating the recruitment of termination factors and removal of elongation marks that block effective termination.