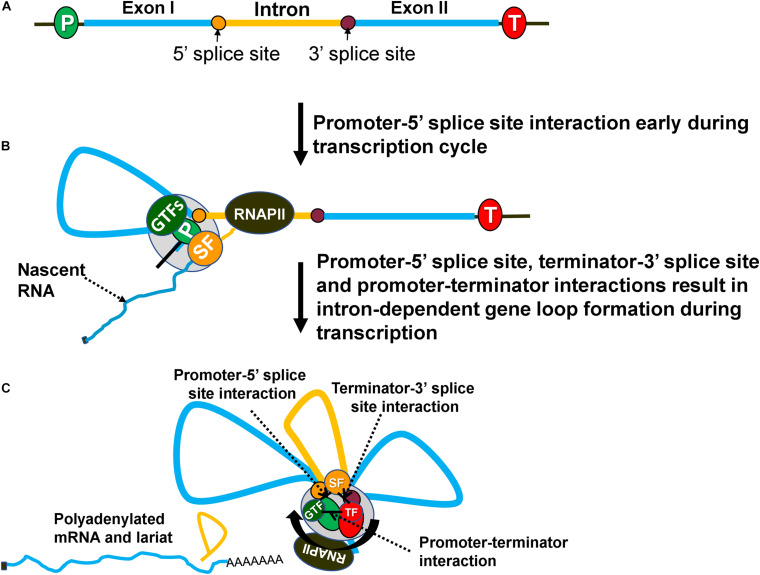
FIGURE 2.
Intron-dependent gene looping enhances transcription by facilitating initiation, reinitiation and promoter directionality. (A) A gene with an intron (yellow) and exons (blue). (B) During transcription, an elongating RNAPII transcribes the gene and recruits splicing factors (SF) to splice out the intervening intronic sequence. Splicing components (SF) at the 5′ splice site interact with the general transcription factors (GTFs) at the promoter forming a loop between the promoter and 5′ splice site. (C) Once RNAPII has transcribed the intron, splicing components at the 3′ splice site associate with the termination factors near the 3′ end of the gene forming a loop between the 3′ splice site and terminator. Finally, the gene forms an overall three-looped conformation where the promoter and terminator physically interact with one another to assist in reinitiation. The three unique interactions that take place are between the promoter-terminator, promoter-5′ splice site and terminator-3′ splice site. GTFs, general transcription factors; SFs, splicing factors; TF, termination factors.