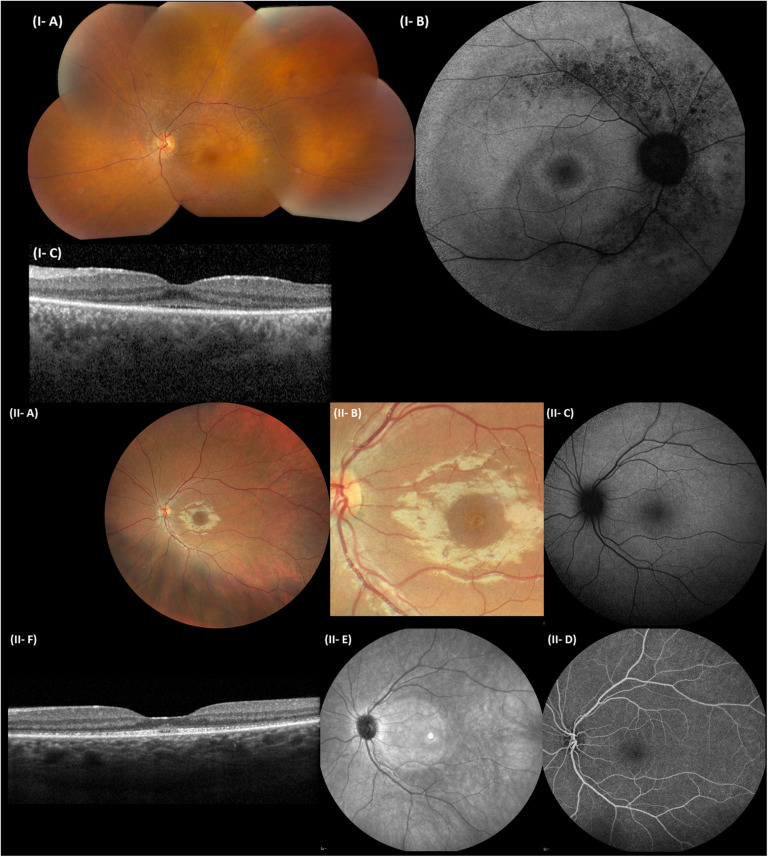
FIGURE 4.
Representative ophthalmological pictures of individuals from F1 and F3 carrying CEP78 structural variants. (I) F1, II:1. (I-A) Color fundus photograph of LE with normal optic disk, minimal narrowing of retinal arterioles, RPE mottling around the temporal vascular arcades, no bone spiculae. (I-B) BAF of the RE with hyperautofluorescent ring surrounding the fovea and granular hypo-autofluorescence around the temporal vascular arcades. (I-C) Spectral-domain OCT of the LE depicting loss of perifoveal photoreceptor layer and better foveal quality with loss, however, of integrity of photoreceptor outer segments. (II) F3, II:1. (II-A) Eye fundus of the left eye with perifoveal fine, granular, yellowish material upon close inspection. Normal aspect of optic disk, peripheral retina, and retinal vessels. (II-B) Close-up of the macular area, demonstrating the fine, granular, yellowish material encircling the fovea. (II-C) BAF of the LE without obvious abnormalities. (II-D) Fluorescein angiography of the LE with normal fluorescence. (II-E) Near-infrared imaging of the LE (hyperintense circular area is an artifact). (II-F) Spectral-domain OCT of the LE, revealing a mottled aspect of the ellipsoid zone and subfoveal collection of fluffy material. Enlarged and flat foveal depression. BAF, blue-light autofluorescence imaging; OCT, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography; RE, right eye; LE, left eye; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.