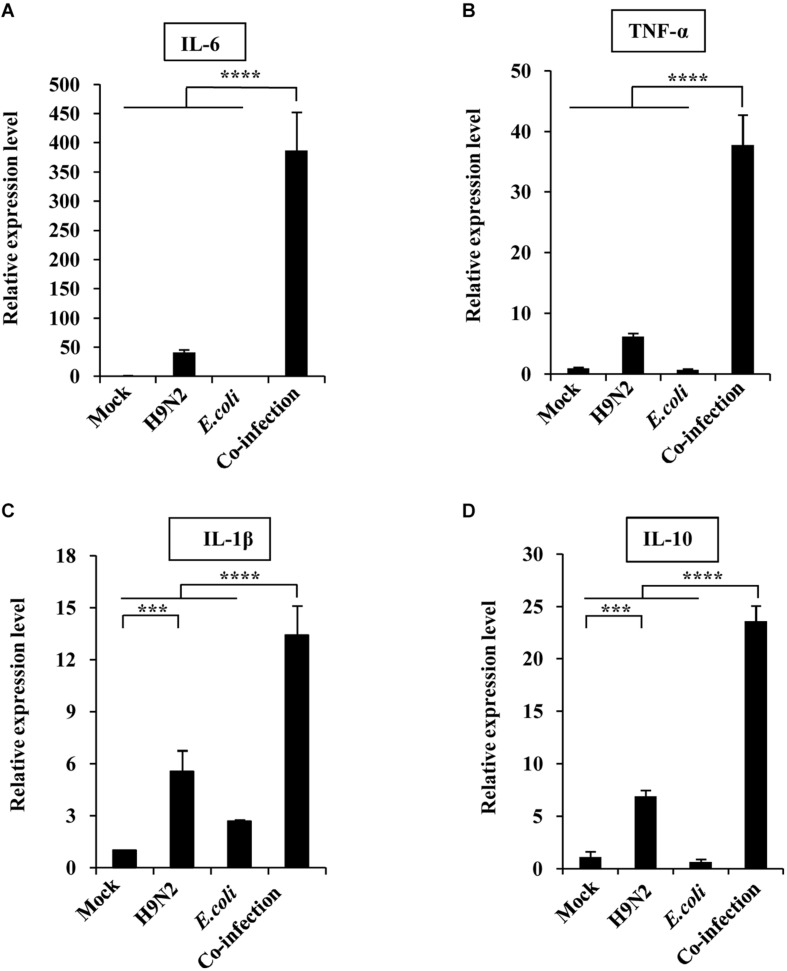
FIGURE 2.
Viral-bacterial co-infection induces excessive expression of inflammatory factors. Four groups of BALB/c mice were mock infected, or intranasally infected with single H9N2 AIV (1 × 104 PFU) and E. coli (1.5 × 107 CFU), or co-infected with H9N2 and E. coli for 48 h. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure the expression of IL-6 (A), TNF-α (B), IL-1β (C), and IL-10 (D) in mouse lungs. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.