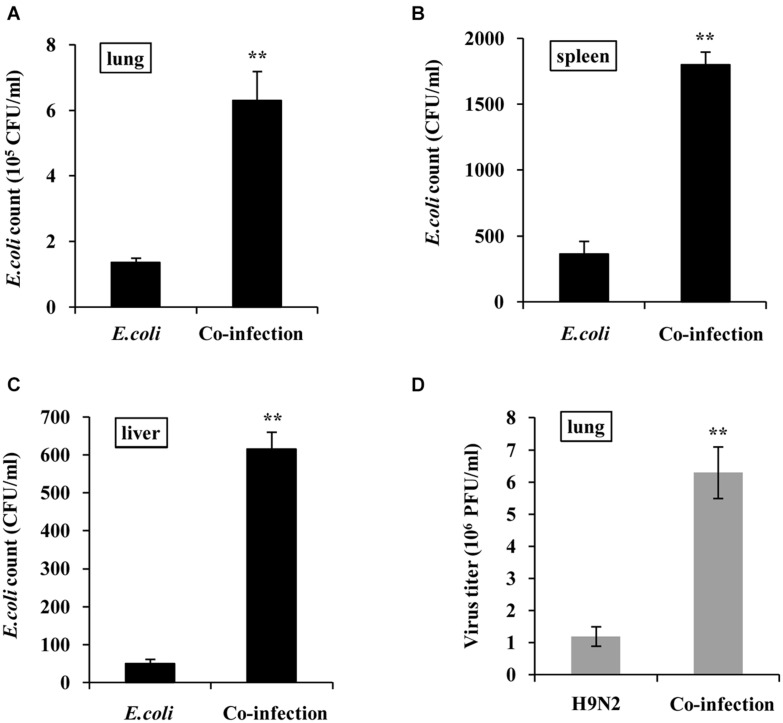
FIGURE 6.
H9N2 and E. coli loads are increased in co-infections. BALB/c mice were intranasally infected with single H9N2 AIV (1 × 104 PFU) and E. coli (1.5 × 107 CFU), or co-infected with H9N2 and E. coli for 48 h. (A–C) Bacterial loads in mouse lungs (A), spleens (B), and livers (C) were measured. (D) Virus titers in mouse lungs were determined by plaque assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.