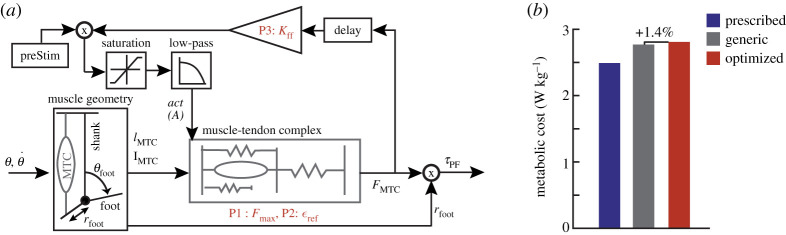
Figure 2.
(a) The neuromuscular controller draws inspiration from biological muscle-tendon parameters and models the geometry of the prosthetic foot and the biological muscle-tendon complex. Two optimization parameters ( and ) affect the force output from the muscle-tendon complex model, with the third optimization parameter serving as the gain on the force output. Based on biological data, was varied from 3000 to 10 000 N, and from 0.03 to 0.14. Based on prior work, varied from 0.7 to 1.5. (b) The metabolic cost results indicate that the optimized controller was the most costly, followed by the generic controller, and then the prescribed prosthesis. Adapted from: Eilenberg et al. [34].