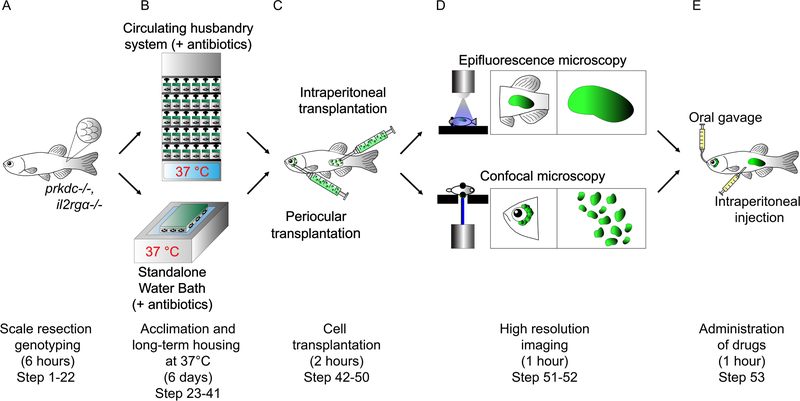
Figure 1. Schematic of a xenotransplantation experiment using prkdc−/−, il2rgα−/− adult zebrafish.
(A) Incrossed progeny from prkdc−/−, il2rgα+/− matings are genotyped at 2.5–3 months of age using a minimally invasive scale resection approach (step 1–22). (B) Following DNA extraction, PCR, and digestion analysis, verified prkdc−/−, il2rgα−/− mutant animals are acclimated to 37 °C for long-term housing using either a stand-alone heated fish system with automatic antibiotic dosing (step 25 option A) or 8L tanks heated to 37 °C using a general purpose water bath (step 25 option B) (step 23–41). (C) Acclimated prkdc−/−, il2rgα−/− zebrafish are then transplanted with fluorescent labeled cells into the intraperitoneal cavity (step 49 option A) or the periocular musculature (step 49 option B) (step 42–50). (D) Animals are then imaged by epifluorescence (step 52 option A) or confocal microscopy (step 52 option B) to assess relative tumor growth over time, respectively (step 51–52). (E) Engrafted prkdc−/−, il2rgα−/− zebrafish can also be subjected to clinically relevant drug dosing by either oral gavage (step 53 option A) or intraperitoneal injection (step 53 option B) (step 53).