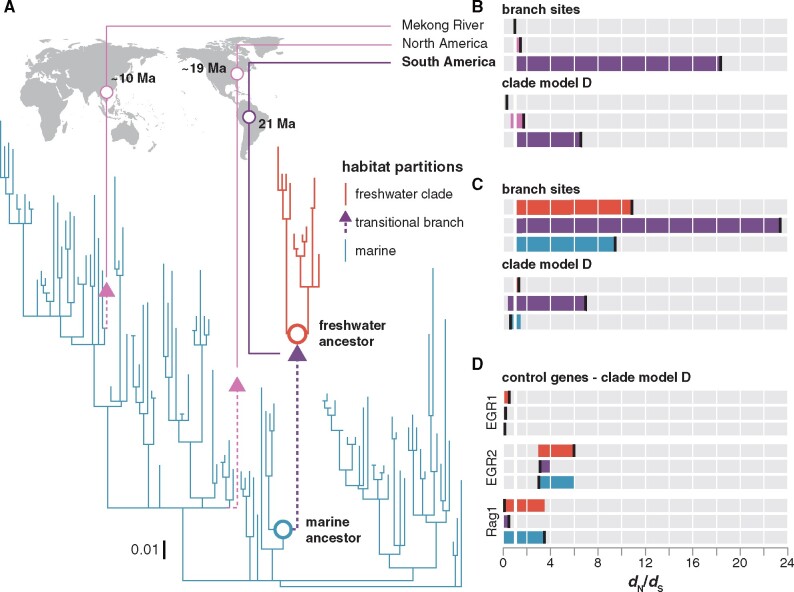
Fig. 2.
Tests for positive selection on rhodopsin associated with habitat transitions. (A) Bayesian phylogeny used for PAML analyses. Branch lengths scaled by the number of substitutions per codon. Divergence time estimates for invasions into freshwater from Lo et al. (2015). (B) Branch sites and CmD dN/dS estimates for the divergent site class with the marine to freshwater transitional branches in the world-wide croaker rhodopsin data set as the foreground. Each bar is colored to match foreground which is indicated by a vertical black bar. (C) Branch sites and CmD dN/dS estimates for the divergent site class for models with the marine lineages, the freshwater clade, and the transitional branch set as the foreground in the New World clade croaker rhodopsin data set. (D) CmD dN/dS estimates for nonvisual control genes using the same ecological partitioning scheme.