Figure 6.
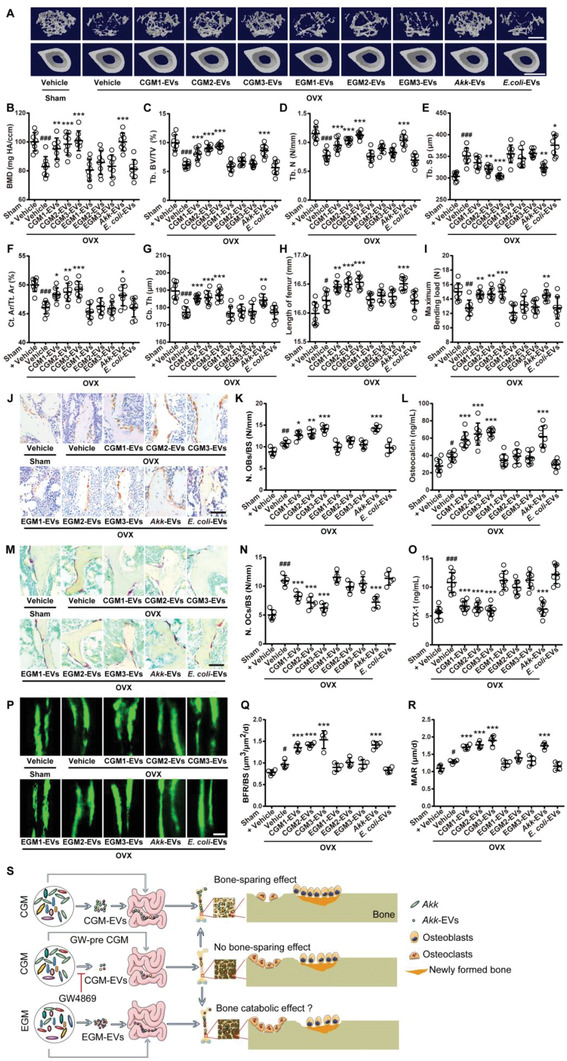
CGM‐EVs and Akk‐EVs protect against OVX‐induced osteoporosis after oral administration. A) Representative µCT images of trabecular (up) and cortical (bottom) bone in femora from Sham and OVX mice receiving vehicle or different EVs by oral route. Scale bars: 500 µm (up) and 1 mm (bottom). Quantification of B) BMD, C) Tb. BV/TV, D) Tb. N, E) Tb. Sp, F) Ct. Ar/Tt. Ar, and G) Ct. Th. n = 8 per group. H) Lengths of femora. n = 8 per group. I) Femur ultimate load measured by three‐point bending test. n = 8 per group. J) Representative OCN‐stained sections with quantification of K) osteoblast number. Scale bar: 50 µm. n = 5 per group. L) ELISA for serum OCN. n = 8 per group. M) Representative TRAP‐stained sections with quantification of N) osteoclast number. Scale bar: 50 µm. n = 5 per group. O) ELISA for serum CTX‐I. n = 8 per group. P) Representative images of calcein double labeling with quantitation of Q) BFR/BS and R) MAR. Scale bar: 10 µm. n = 4 per group. S) Schematic diagram summarizing the major findings of this study. Data are presented as mean ± SD. # P < 0.05 versus Sham + Vehicle group, * P < 0.05 versus OVX + Vehicle group. #/* P < 0.05, ##/** P < 0.01, and ###/*** P < 0.001.
