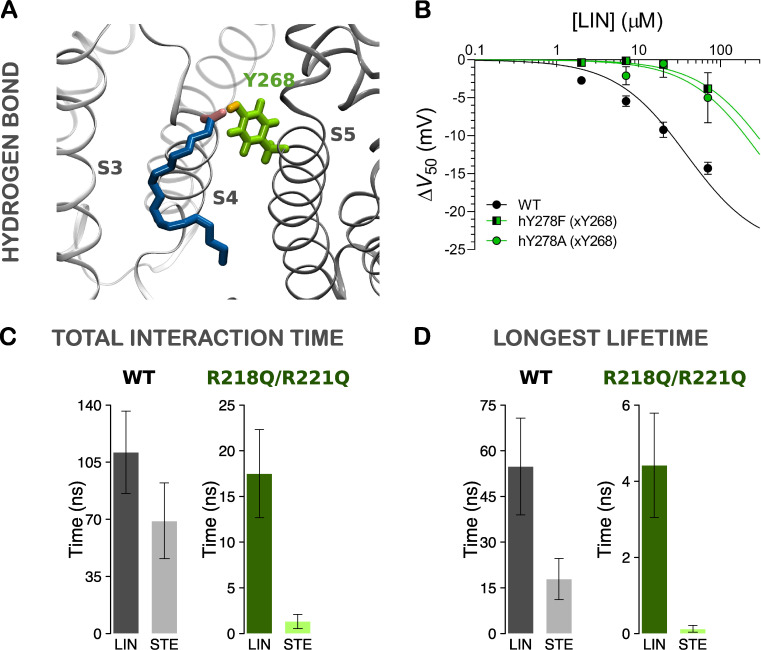
Figure 5.
Hydrogen bonding of LIN and STE head groups to S5 tyrosine comparing the WT (S4 up) and R218Q/R221Q (pseudo S4 down) systems. (A) Side view of a LIN head group interacting with the S5 tyrosine Y268 at site I in the R218Q/R221Q system, which is a pseudo-resting state of S4 generated by mutating in silico the two top arginines in S4. (B) Experimental mutation of tyrosine hY278 (xY268) impairs the effect of LIN. Data shown as mean ± SEM; n = 4–7 per data point. Concentration-response curves were fitted using Eq. 2 with the Hill coefficient constrained to −1 (see Materials and methods for details). ΔV50,max was constrained to −25 mV to make the fits more robust. (C and D) Total interaction time (C) and longest lifetime (D) of hydrogen bonds between the FA negatively charged head group and Y268 in 500 ns of AA MD of WT and R218Q/R221Q systems. Data shown as mean ± SEM. ΔV50,max denotes maximal effect in ΔV50.