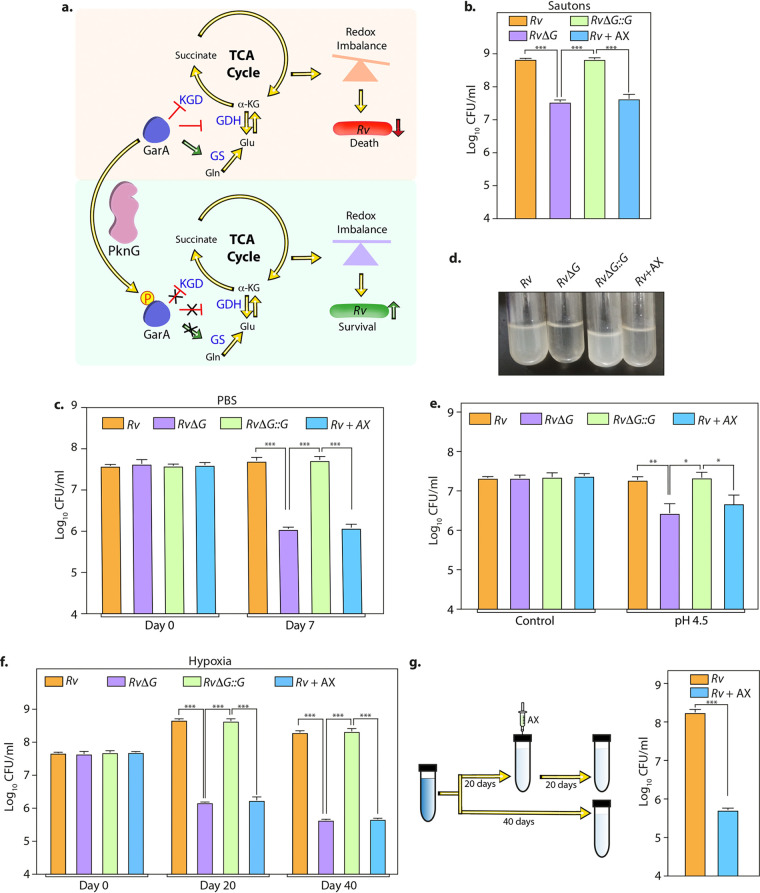
FIG 1.
AX inhibits Mtb survival in the in vitro models of latency. (a) Model illustrating the role of PknG during latency. GarA, a central metabolic regulator, inhibits α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) decarboxylase (KGD) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and activates glutamate synthase (GS). The phosphorylation of GarA by PknG alleviates the inhibition of KGD and GDH and the activation of GS. The PknG-GarA signaling axis is necessary for fine-tuning the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and glutamate metabolism, thus maintaining cellular redox homeostasis and abetting the survival of Mtb under latency-like conditions. (b to f) In the case of Rv plus AX (Rv+AX), 1 mM AX was added to Rv at the start of the experiment. (b) Rv, RvΔG, Rv+AX, and RvΔG::G were inoculated at an A600 of ∼0.1 in Sauton’s medium, and bacillary survival was enumerated at day 6. (c) Early-log-phase cultures were resuspended in PBS, and CFU were enumerated on day 7. (d) Pictorial representation of the growth of the indicated strains in acidified 7H9-ADC medium at day 7. (e) Single-cell suspensions of Rv, RvΔG, Rv+AX, and RvΔG::G were inoculated at an A600 of ∼0.1 in acidified 7H9-ADC medium, and CFU were enumerated on day 7. (f) Bacterial strains were inoculated at an A600 of ∼0.1 in 7H9-ADC medium containing methylene blue in tightly sealed tubes. CFU were enumerated on days 0, 20, and 40. (g) Schematic representation of the hypoxia experiment. Twenty days after the start of the experiment, 1 mM AX was injected using a fine needle, and tubes were resealed. A parallel group was left untreated (Rv). CFU were enumerated on day 40. Bars depict means ± SD (n = 3), representative of data from two biologically independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.