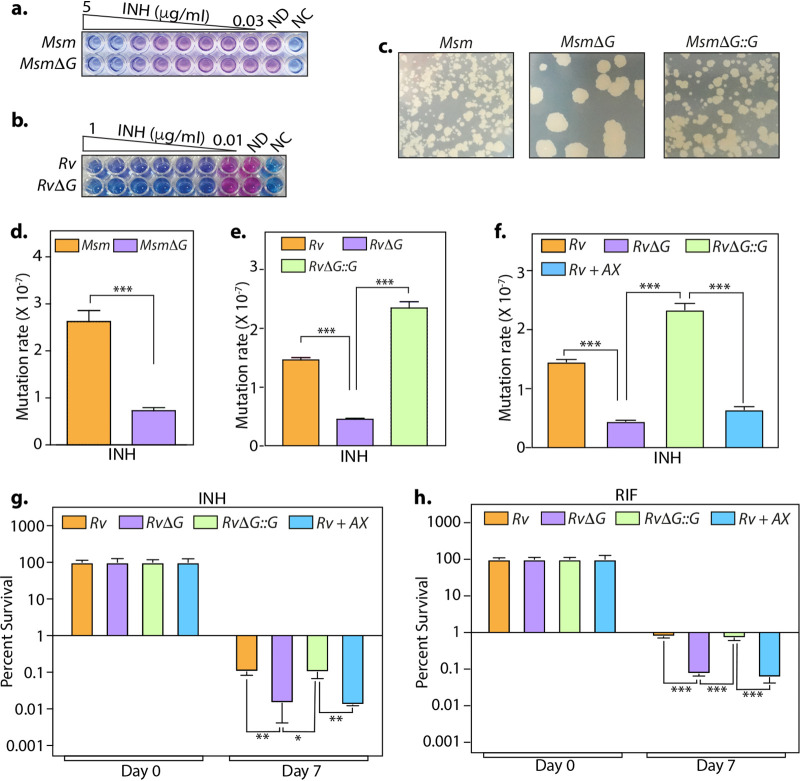
FIG 2.
Inhibition of PknG suppresses the emergence of drug-resistant and -tolerant cells. (a and b) The sensitivities of wild-type and pknG mutant Msm (a) and Mtb (b) strains to INH were determined with the help of an alamarBlue assay. ND and NC indicate no-drug and no-cell controls, respectively. (c) A total of 108 cells of Msm, MsmΔG, and MsmΔG::G were plated on 7H11-OADC plates containing 10 μg/ml isoniazid. (d and e) The antibiotic resistance frequency was determined by spotting 108 cells of Msm (d) and Mtb (e) strains on 7H11-OADC plates containing 100 μg/ml (d) and 10 μg/ml (e) INH, respectively. (f) Experiment performed as described above for panel e, with 1 mM AX added to Rv, where indicated. For panels d to f, the mutation rate is calculated as the number of colonies obtained on antibiotic-containing plates/number of colonies obtained on plain plates. The bar diagram represents means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) and is representative of results from a minimum of two independent biological replicates (n = 7). (g and h) Mtb strains were inoculated in 7H9-ADS medium containing 5 μg/ml INH (g) or 1 μg/ml RIF (h). Survival was monitored on days 0 and 7, and the survival obtained at day 0 was normalized to 100%. Percent survival at day 7 was calculated with respect to survival at day 0 for each strain. Data are represented as mean percent survival ± SD from one of three biologically independent experiments, each performed in triplicates (n = 3). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.