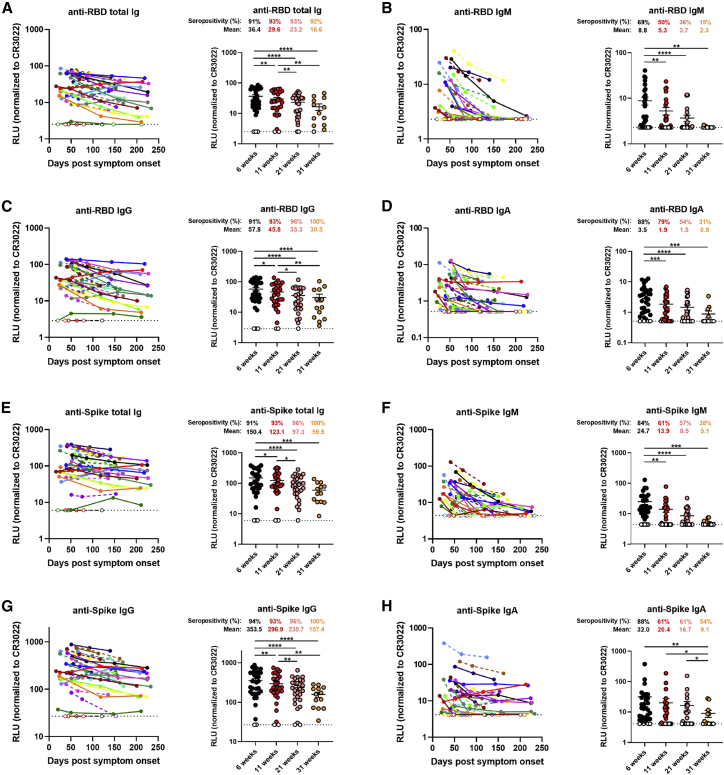
Figure 1.
Decline of RBD- and Spike-specific antibodies in longitudinal convalescent plasma
(A–D) Indirect ELISA was performed using recombinant SARS-CoV-2 RBD protein and incubation with COVID-19+ plasma samples recovered between 6 and 31 weeks post-symptom onset. Anti-RBD antibody binding was detected using horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated (A) anti-human IgM+IgG+IgA, (B) anti-human IgM, (C) anti-human IgG, or (D) anti-human IgA. Relative light unit (RLU) values obtained with BSA (negative control) were subtracted and further normalized to the signal obtained with the anti-RBD CR3022 monoclonal antibody (mAb) present in each plate.
(E–H) Cell-based ELISA was performed using HOS cells expressing full-length SARS-CoV-2 Spike and incubation with COVID-19+ plasma samples recovered between 6 and 31 weeks post-symptom onset. Anti-Spike antibody binding was detected using HRP-conjugated (E) anti-human IgM+IgG+IgA, (F) anti-human IgM, (G) anti-human IgG, or (H) anti-human IgA. RLU values obtained with parental HOS (negative control) were subtracted and further normalized to the signal obtained with the CR3022 mAb present in each plate.
(Left panels) Each curve represents the normalized RLUs obtained with the plasma of one donor at every donation as a function of the days after symptom onset. (Right panels) Plasma samples were grouped in different time points post-symptom onset (6, 11, 21, and 31 weeks). Undetectable measures are represented as white symbols, and limits of detection are plotted. Error bars indicate means ± SEM. Statistical significance was tested using repeated-measures one-way ANOVA with a Holm-Sidak post-test (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).