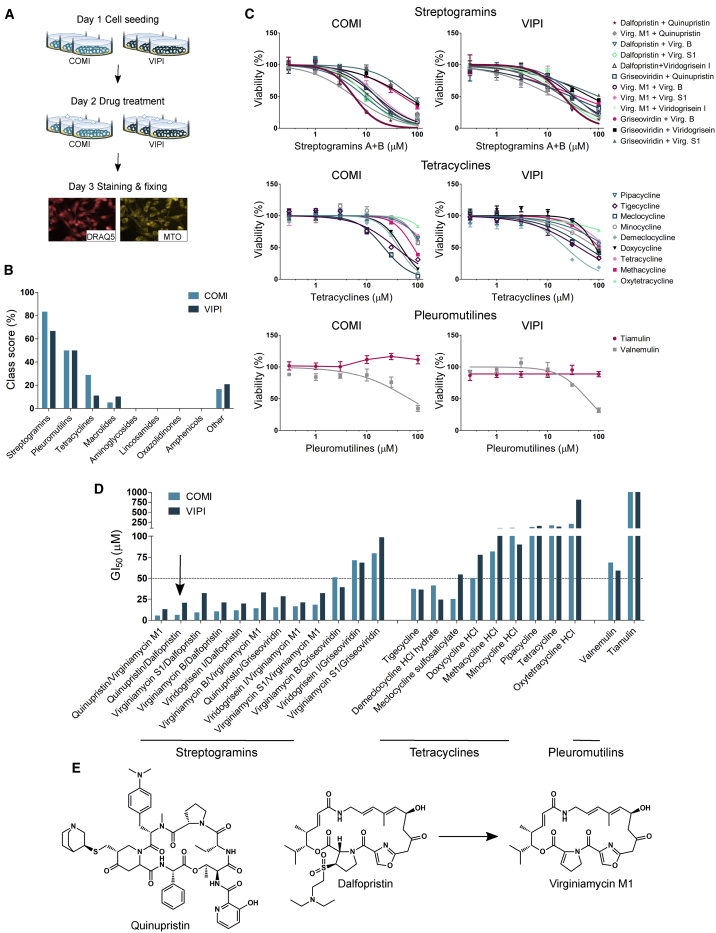
Figure 1.
Q/D is the most effective prospective mitochondrial translation inhibitor in GSCs
(A) An outline of the screening workflow. Each treatment was performed in a technical triplicate.
(B) Identification of hit classes based on class score calculation.
(C) Representative dose-response curves for all tested compounds belonging to the three hit classes validated in COMI and VIPI cells; n = 4 technical replicates, mean ± SD.
(D) The GI50 values of the tested compounds.
(E) The chemical structures of the lead compound Q/D (30:70 w/w) and virginiamycin M1, the product of dalfopristin hydrolysis.
See also Figures S1 and S2 and Tables S1–S3.