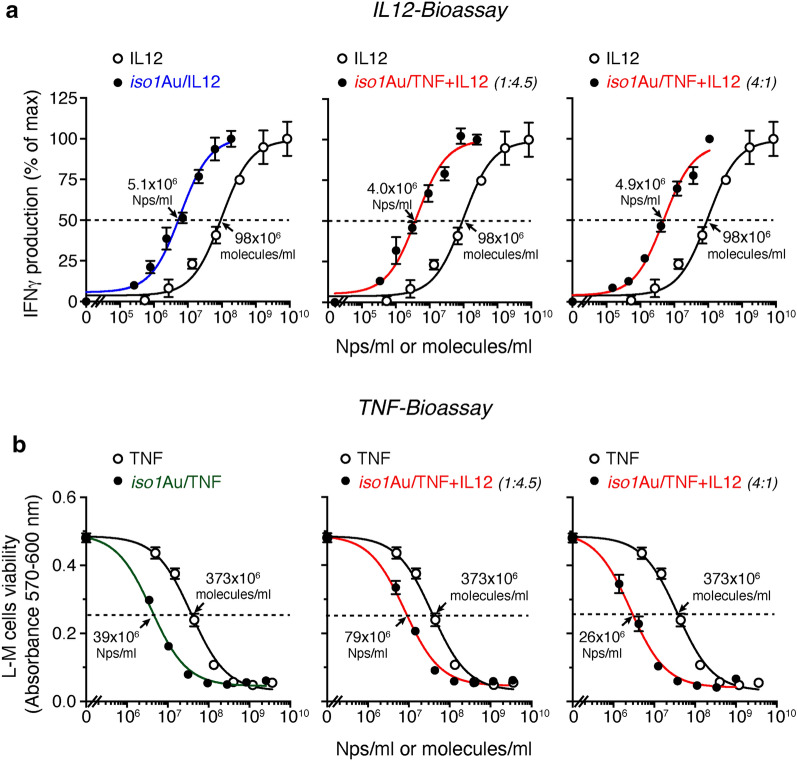
Fig. 2.
Biological effects of bi- and trifunctional nanodrugs on IFNγ production by splenocytes (a) and L–M cell viability (b). a Effect of nanodrugs and IL12 on IFNγ production by murine splenocytes. Murine splenocytes (200,000 cells in 200 µl of culture medium) were cultured in complete medium supplemented with 125 U/ml of IL-2 and variable amounts of nanodrugs or IL12 for 5 days. IFNγ production in pooled cell supernatants (prepared in quadruplicate) was determined by ELISA (in duplicate). One representative experiment is shown (mean ± SE). The cumulative data of 4–12 experiments are reported in Table 2. The TNF:IL12 ratio used to prepare the trifunctional nanodrug is indicated in parentheses. Arrows, effective concentration 50 (EC50). b Cytotoxic effects of nanodrugs and TNF on L–M cells. L–M cells (30,000 cells in 100 µl of culture medium) were cultured in complete medium supplemented with 2 µg/ml of actinomycin D and the indicated amounts of nanodrugs or TNF for 20 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Cell viability was quantified using the PrestoBlue Cell Viability Reagent. One representative experiment is shown (mean ± SE, of triplicates). The cumulative data of 3–7 experiments are reported in Table 2