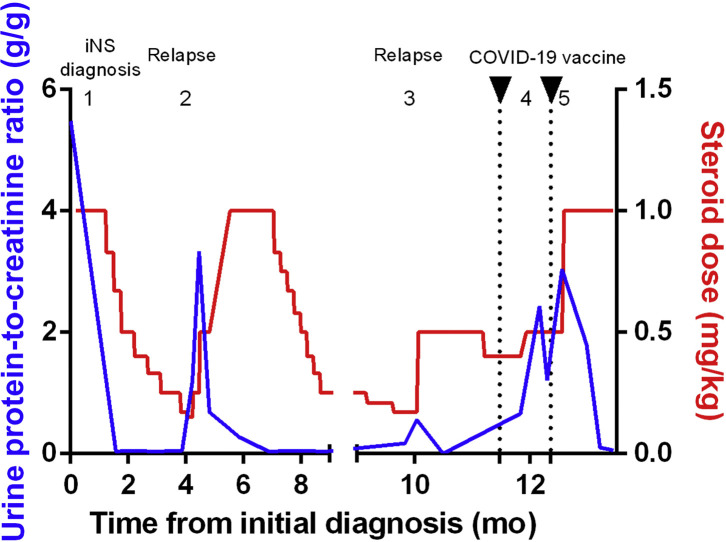
Figure 1.
Urine protein-to-creatinine ratio and steroid dose during follow-up. (1) Diagnosis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (iNS; minimal change disease diagnosed on kidney biopsy). (2) First relapse when tapering steroids from 10 mg to 9 mg; increase of steroid dose to 1 mg/kg (60 mg), leading to remission of NS. (3) Second relapse when tapering steroids from 12.5 mg to 10 mg; increase of steroid dose to 0.5 mg/kg, leading to remission. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccine was injected while the patient was treated with 0.4 mg/kg steroids (25 mg; ongoing tapering from last relapse occurring 6 weeks before first vaccine injection; no proteinuria on urine dipstick test at the time of vaccine injection). (4) Proteinuria after first mRNA COVID-19 vaccine injection; increase of steroid dose from 25 mg to 30 mg (0.5 mg/kg). (5) Proteinuria increase after second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine injection; increase of steroids to 60 mg (1 mg/kg), leading to remission.