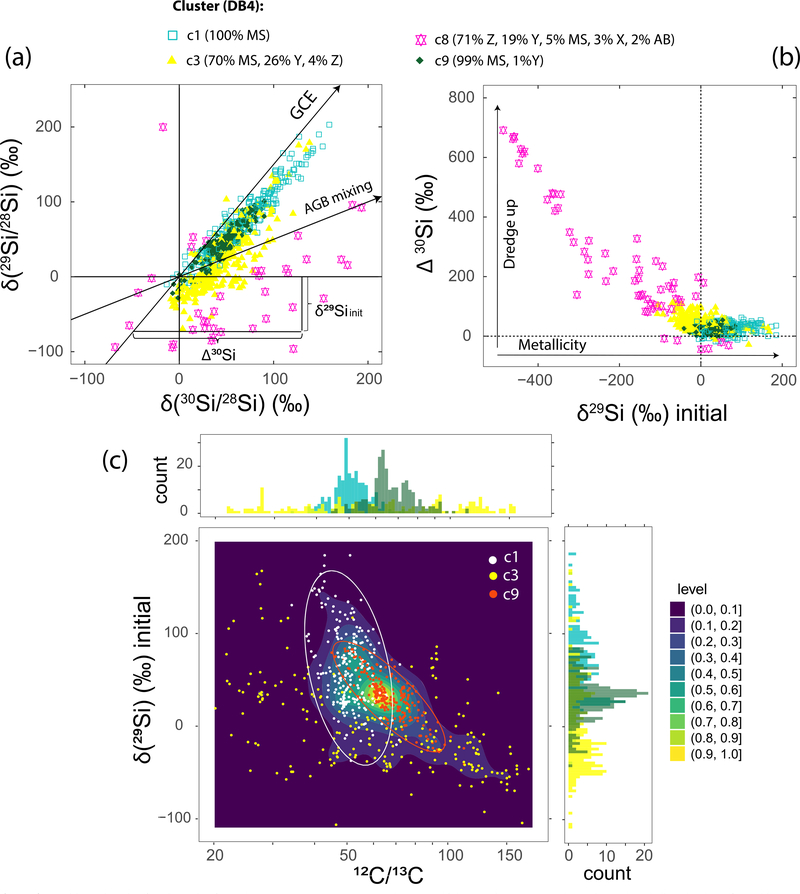
Figure 4.
(a) Si isotopic ratios for SiC grains from clusters c1DB4, c3DB4, c8DB4, and c9DB4, which comprise MS, Y, and Z grains and are believed to have formed in AGB stars. Solid arrows show the GCE trend we assumed to represent the initial composition of the parent star, and the AGB mixing line, reflecting changes in grain composition due to dredge-up events (Nittler & Alexander 2003). Here, we considered a GCE line slope of 1.5 and intersecting the solar composition, and a mixing line with a slope of 0.5, following (Nittler & Alexander 2003). The initial δ29Si and the degree of AGB mixing (estimated with Δ30Si) were calculated using these lines and are shown in panels (b) and (c) with C isotopic ratios. In panel (c), we also plotted the density distribution of the data (highest and lowest in yellow and dark blue areas), and histograms for 12C/13C and initial δ29Si for the three selected clusters. White and orange ellipses are guidelines showing clusters c1DB4 and c9DB4, respectively.