Figure 4. In vivo therapeutic efficacy in MRSA muscle infection.
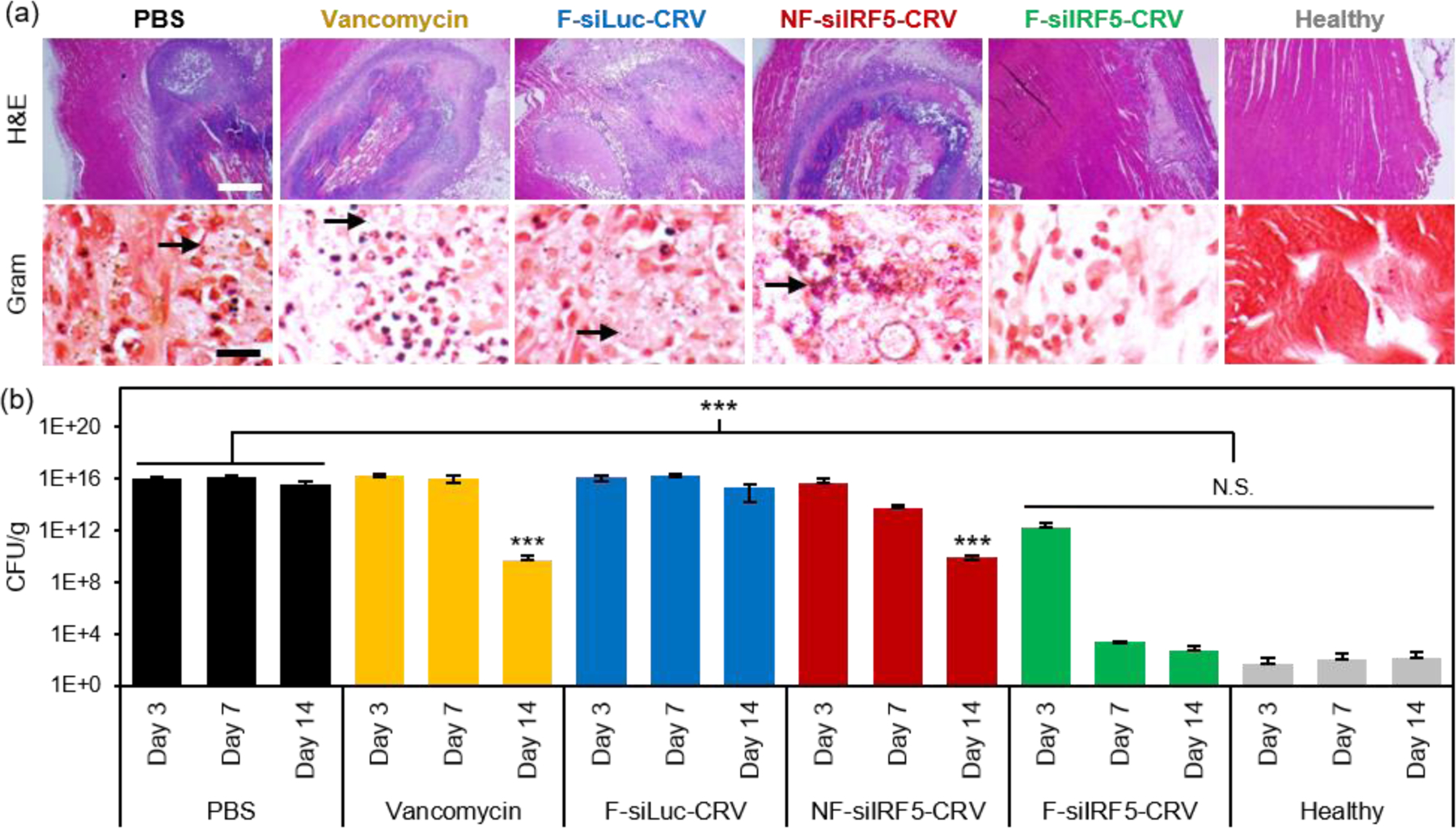
(a) H&E (top) and Gram (bottom) stains of infected muscle tissues from mice 7 days after treatment with PBS, vancomycin, non-fusogenic, targeted pSiNPs containing siIRF5 (NF-siIRF5-CRV), fusogenic, CRV-targeted pSiNPs containing siRNA against luciferase, as a negative control for siIRF5 (F-siLuc-CRV), and fusogenic, CRV-targeted pSiNPs containing siIRF5 (F-siIRF5-CRV); scale bar represents 1 mm (top row) and 100 μm (bottom row); (b) Bacterial titer (CFU per mass of tissue) from muscles of healthy and MRSA-infected mice intravenously injected with the treatment formulations as indicated. Animals were infected on day 0 and therapeutic or control injections were given on day 1. Mice were sacrificed for titer counts at days 3, 7, and 14 days post-intravenous injection. Bars indicate standard deviation with n = 6. N.S. represents no significance and *** represents p < 0.01 relative to the PBS group from one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc analyses.
