Figure 2. An ensemble model for sequence variation at a specific site in a native protein.
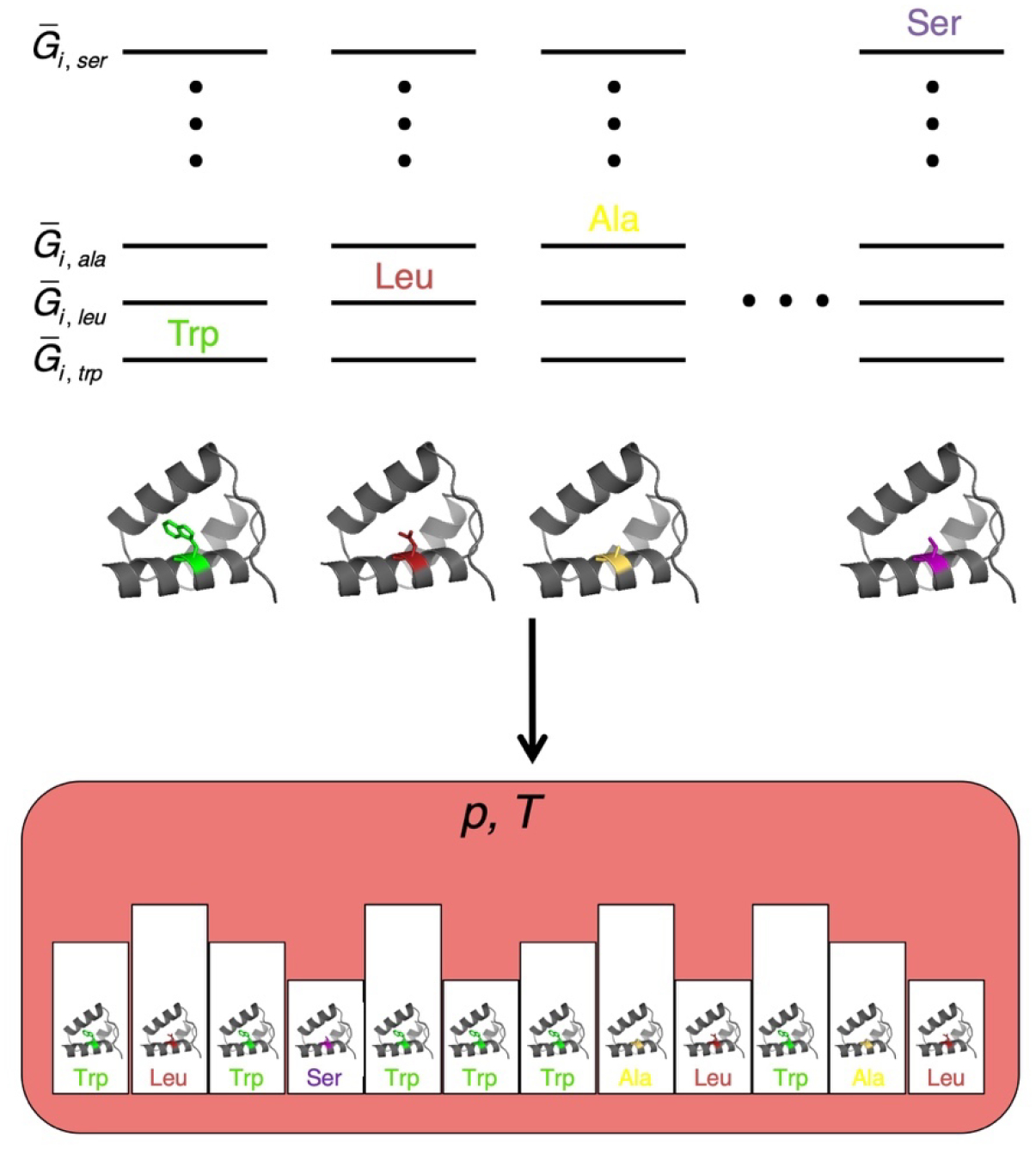
(Top) Gibbs free energy values (where the overbar indicates molar energies) for each of the 20 residues (plus a gap) at position i in the native state. Each side-chain free energy is determined by specific interactions between the side chain and the protein and solvent in all conformations available to the side chain. (Bottom) an isothermal isobaric ensemble (defined by the temperature and pressure of a large reservoir, pink) containing single-chain replicas that can exchange heat and volume with the reservoir. Side chains are allowed to equilibrate over the set r through alchemical transformation, producing equilibrium populations that reproduce residue frequencies at site i in an MSA, and are related to side-chain free energies through Boltzmann-like terms. For simplicity, only the four residues from panel A are shown.
