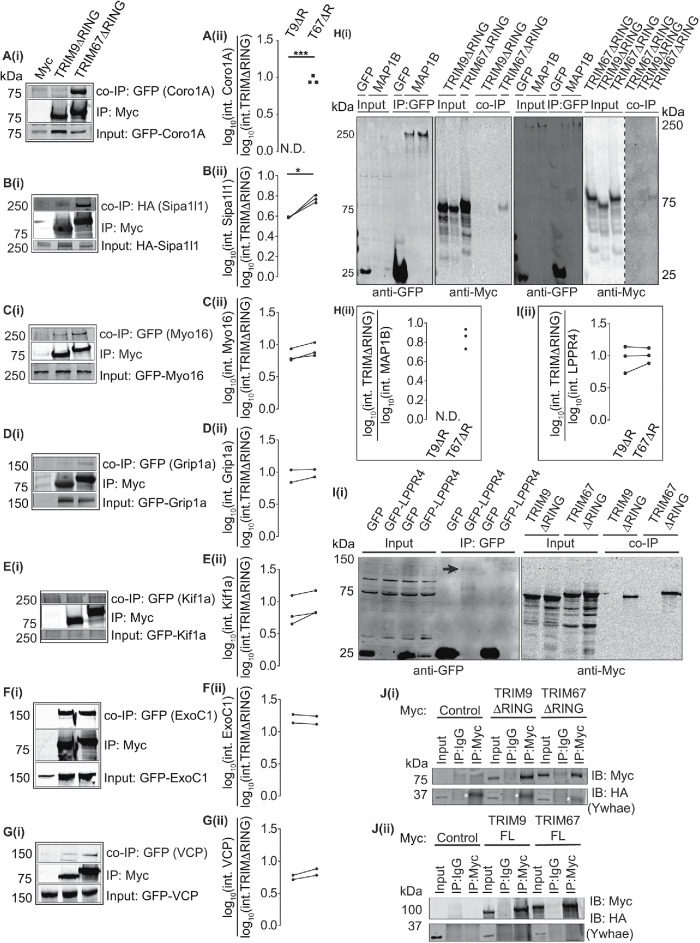
FIGURE 3:
Validation of potential TRIM9 and TRIM67 interaction partners via co-IP assays. (A–G) Immunoblots showing co-IP of GFP- or HA-tagged proteins when immunoprecipitated using an anti-Myc antibody to enrich for Myc, Myc-TRIM9∆RING, or Myc-TRIM67∆RING. (A: Coro1A [n = 3], B: Sipa1l1 [n = 3], C: Myo16 [n = 3], D: GRIP1a [n = 2], E: Kif1a [n = 3], F: ExoC1 [n = 2], G: VCP [n = 2]). A(i) –G(i) show blots for inputs for the coimmunoprecipitated proteins, the immunoprecipitated Myc-TRIM9ΔRING or Myc-TRIM67ΔRING and co-IP proteins. A(ii) –G(ii) show individual datapoints of co-IP GFP- or HA-tagged proteins relative to Myc-TRIM9ΔRING (T9ΔR) or Myc-TRIM67ΔRING (T67ΔR). (H(i)) Immunoblot demonstrating co-IP of Myc-TRIM67∆RING, but not Myc-TRIM9∆RING with GFP-MAP1B. Two representative blots are included, one with GFP-control coexpressed with Myc-TRIM9∆RING and one with GFP-control coexpressed with Myc-TRIM67∆RING. H(ii) shows individual datapoints of co-IP Myc-TRIM67ΔRING (T67ΔR) relative to GFP-MAP1B (n = 3). Myc-TRIM9∆RING (T9ΔR) did not coprecipitate with GFP- MAP1B (N.D.). (Ii) Immunoblot showing Myc-TRIM9∆RING and Myc-TRIM67ΔRING co-IP with GFP-LPPR4 (PRG-1). The black arrow in the blot probed for GFP shows a faint GFP-LPPR4 band. Note that GFP-LPPR4 was not detected in inputs. I(ii) shows individual datapoints of coimmunoprecipitated Myc-TRIM9∆RING (T9ΔR) and Myc-TRIM67ΔRING (T67ΔR) relative to GFP-LPPR4 (n = 3). (J(i), (ii)) Immunoblots demonstrating that HA-Ywhae does not coimmunoprecipitate with Myc-TRIM∆RING (n = 3) or full-length constructs of TRIM9 and TRIM67 (n = 3). The white asterisks in J(i) denote a nonspecific band observed in all anti-Myc IP lanes. Datapoints were compared using an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction, *, P < 0.05, ***, P < 0.005.