FIGURE 5:
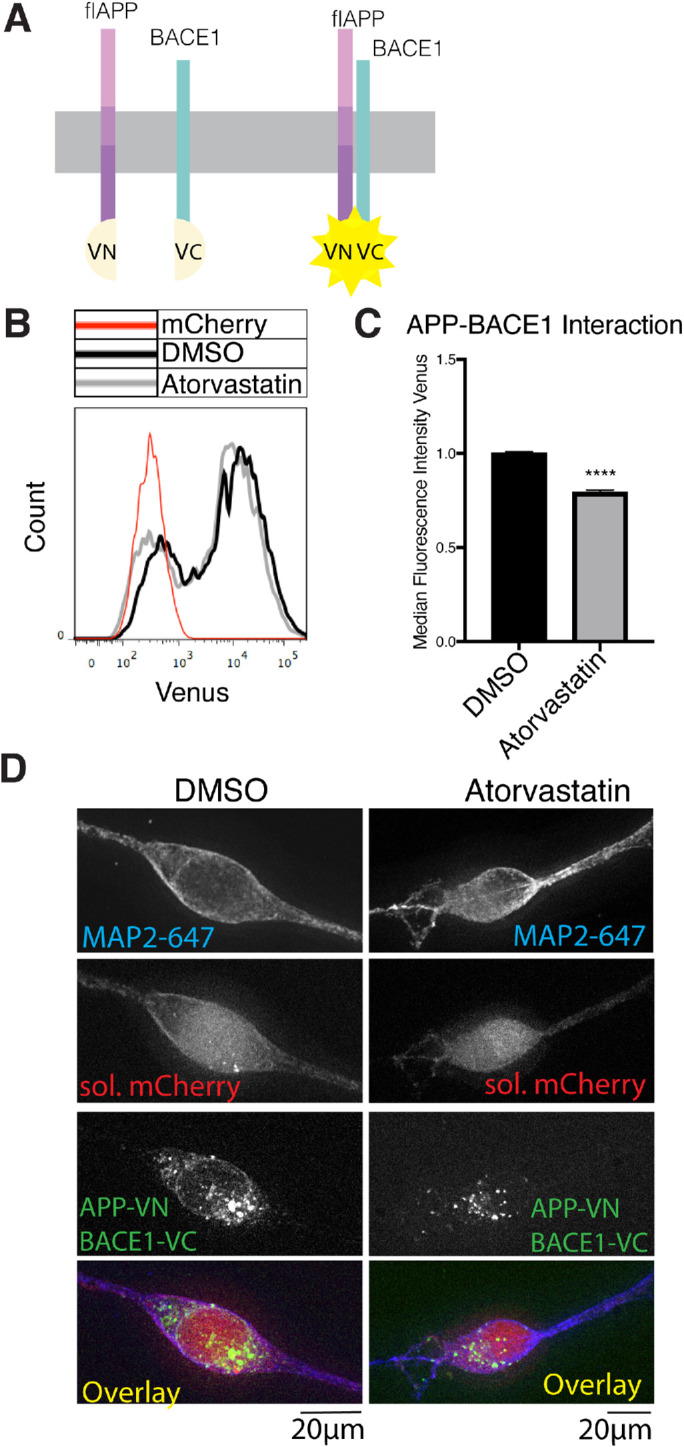
Statins decrease APP-BACE1. Interaction. (A) Principle of the APP-BACE1 interaction assay. The C-terminus of Venus fluorescent protein (vc) was tagged to the C-terminus of BACE1 to generate the BACE1vc plasmid. The N-terminal half of Venus (vn) was tagged to the C-terminus of flAPP to generate the APPvn plasmid. To test the interaction of APP and BACE1, both plasmids are cotransfected into the cells along with a soluble mCherry plasmid for cell selection. When APP and BACE1 interact, vn and vc fragments reconstitute into a functional Venus protein and emit fluorescence, which can be detected by microscopy or flow cytometry. (B, C) HEK cells were plated in DMSO or 10 μM atorvastatin and then transiently transfected 24 h later. Cells were transfected with wtAPPvn, wtAPPvc, and mCherry unless otherwise indicated. mCherry-positive cells were analyzed 16 h after transfection. (B) Histograms showing flow cytometry analysis of BACE1-flAPP interaction (Venus median fluorescence intensity). A negative control transfected with only mCherry is shown in red. (C) Quantification of flow cytometry analysis of BACE1-flAPP interaction (Venus median fluorescence intensity) (mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3). (D) iPSC-derived WT neurons were plated in DMSO or 10 μM atorvastatin. Four days later, neurons were transiently transfected with wtAPPvn, BACE1vc, and mCherry. Cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with MAP2 16 h post-transfection. Cells were selected for imaging based on positive MAP2 and mCherry signal and neuronal morphology. Imaging and image processing were performed blind.
