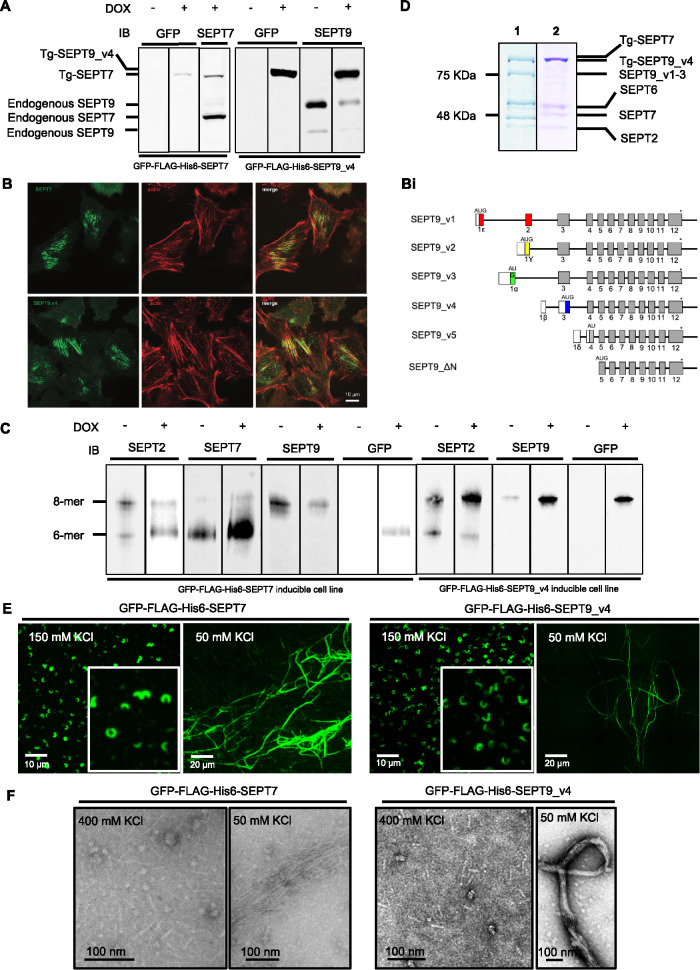
FIGURE 1:
Expressed GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT7 and GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT9_v3 incorporate into endogenous septin filaments. (A) Western Blot of induced GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT7 stable cell line lysate shows two bands (endogenous and transgene [Tg-SEPT7]) when probed with anti-SEPT7 antibody and one band (Tg-SEPT7) when probed with anti-GFP antibody. Hexamer band containing transgene is slightly larger than endogenous due to the presence of tags. Induced GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT9_v4 stable cell line lysate immunoblotted with SEPT9 and GFP antibodies shows three and one bands (endogenous and Tg-SEPT9_v4), respectively, in induced cells. Endogenous SEPT9 has two bands in uninduced cells representing different isoforms. (B) SEPT9 (GFP signal) and actin (phalloidin signal) demonstrating expressed septins associated with stress fibers. (Bi) Schematic representation of different SEPT9 isoforms. The stop codon is represented by an asterisk, noncoding regions by open boxes, isoform-specific sequences by colored boxes and common coding regions by gray boxes. The position of the AUG translational start is indicated above the line (modified from McDade et al., (2007). (C) Septin heteromers of GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT7 and GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT9_v4 induced and uninduced stable cell lines resolved with Blue Native PAGE followed by immunodetection with SEPT2, SEPT7, and SEPT9 and GFP antibodies. Positions of hexamers and octamers determined previously (Sellin et al., 2014) (D) FLAG-immunopurified (1) GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT7 and (2) GFP-FLAG-His6-SEPT9_v4 complex separated by SDS–PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. Protein position determined by Western blotting with specific antibodies (Supplemental Figure S1). (E) Isolated complexes visualized by fluorescence microscopy in elution buffer (150 mM KCl) or following dialysis in low salt (50 mM KCl). (F) EM of isolated complexes in high salt (400 mM KCl) and low salt buffer (50 mM KCl) following negative staining with uranyl acetate.