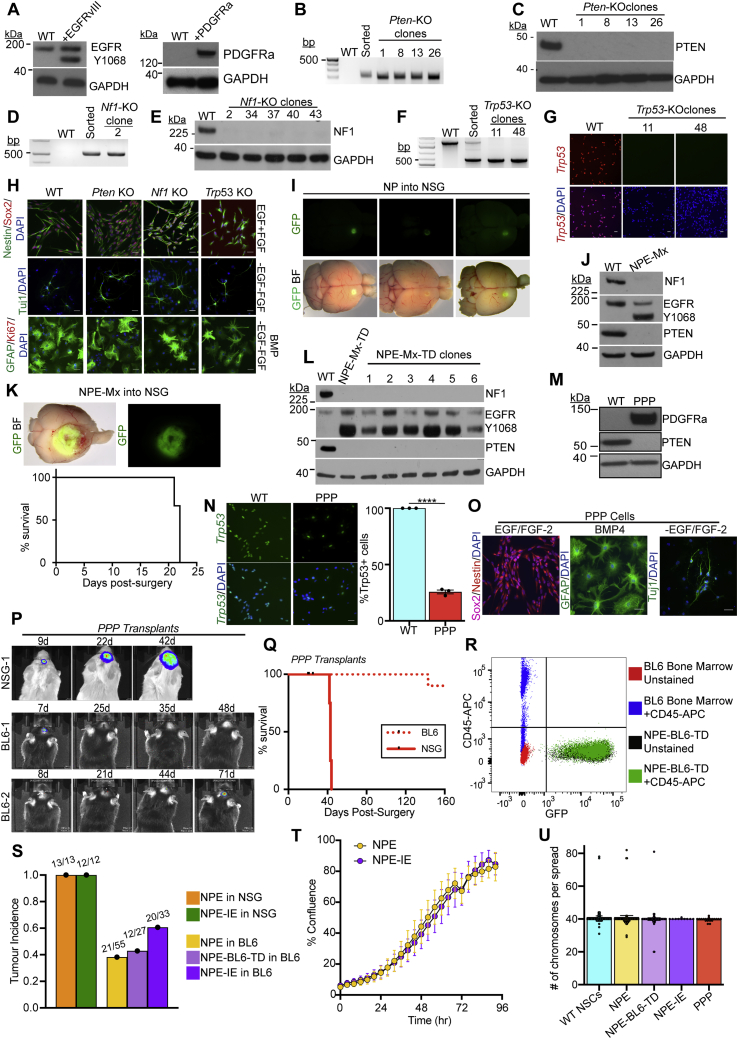
Figure S1.
Engineering GBM driver mutations in adult mouse neural stem cells to create GBM initiating cell lines, related to Figure 1 and Table S1
(A) Immunoblots of EGFRvIII (left panel) and PDGFRa (right panel) overexpression in NSCs following transfection with the PB-Transposon plasmids.
(B) PCR genotyping of clonal Pten Knock-Out (KO) lines to confirm successful gene targeting.
(C) Immunoblot of Pten KO NSC lines confirms loss of PTEN protein expression.
(D) PCR genotyping of clonal Nf1 KO lines to confirm successful gene targeting.
(E) Immunoblot of Nf1 KO NSC lines confirms loss of NF1 protein expression.
(F) PCR genotyping of clonal Trp53 KO lines to confirm successful gene targeting.
(G) ICC analysis of Trp53 KO clones confirms loss of TRP53 expression, scale bar = 20μm.
(H) CRISPR KO of Pten, Nf1 and Trp53 in NSCs does not affect the expression of the common NSC markers Nestin or SOX2, or the ability of NSCs to respond to differentiation cues (growth factor withdrawal and/or BMP addition), scale bar = 20μm.
(I) Orthotopic transplantation of NP cells into NOD-scid-gamma (NSG) mice provides a premalignant model (whole brain live imaging shown; top, GFP; bottom, overlay of GFP and brightfield (BF), representative images of n = 5 mice).
(J) Immunoblots of the GBM driver mutations (NF1, PTEN and EGFRvIII) in engineered NPE-Mx (multiplex) NSCs.
(K) Top: Orthotopic transplantation of NPE-Mx cells leads to tumour formation in NSG mice (whole brain live imaging shown; top, GFP; bottom, overlay of GFP and brightfield (BF)). Bottom: Survival curve of NSG mice orthotopically transplanted with NPE-Mx cells (n = 3 mice).
(L) Immunoblots of NF1, PTEN, and EGFR expression in NPE-Mx-TD (tumour-derived) polyclonal and clonal lines versus parental NSCs.
(M) Immunoblot of PDGFRa and PTEN in PPP NSCs.
(N) ICC confirming reduction of TRP53 expression in PPP cells versus parental NSCs (left panel) and quantification of Trp53-expressing cells by ICC (right panel; student’s t-test ∗∗∗ p≤0.001, error bars represent SEM), scale bar = 20μm.
(O) ICC of PPP mutant NSC lines for NSC markers (Sox2, Nestin) in self-renewing, EGF/FGF containing media and differentiation markers (GFAP, Tuj1) in differentiation conditions (BMP or -EGF/-FGF), scale bar = 20μm.
(P) Bioluminescent IVIS imaging of PPP tumour progression in vivo in NSG and BL6 recipients. Number of days post-surgery is noted above each image.
(Q) Survival curve of NSG (n = 4) and BL6 (n = 15) mice transplanted with PPP cells
(R) Flow cytometric analysis of the NPE-BL6-TD cells confirms that no CD45+ cells are detectable in vitro as compared to unstained NPE-BL6-TD and bone marrow-derived cells.
(S) Quantification of tumour incidence in NSG and BL6 mice transplanted with NPE, NPE-BL6-TD and NPE-IE cell lines. Numbers above bars denote actual tumour occurrence in all transplants.
(T) Confluence analysis of NPE and NPE-IE cells indicates no significant difference in proliferation rates (p = 0.2888).
(U) Karyotyping of parental subsequently engineered NSCs (>10 cell spreads counted per cell line, bars represent the mean value, error bars represent SEM, dots represent individual counts).