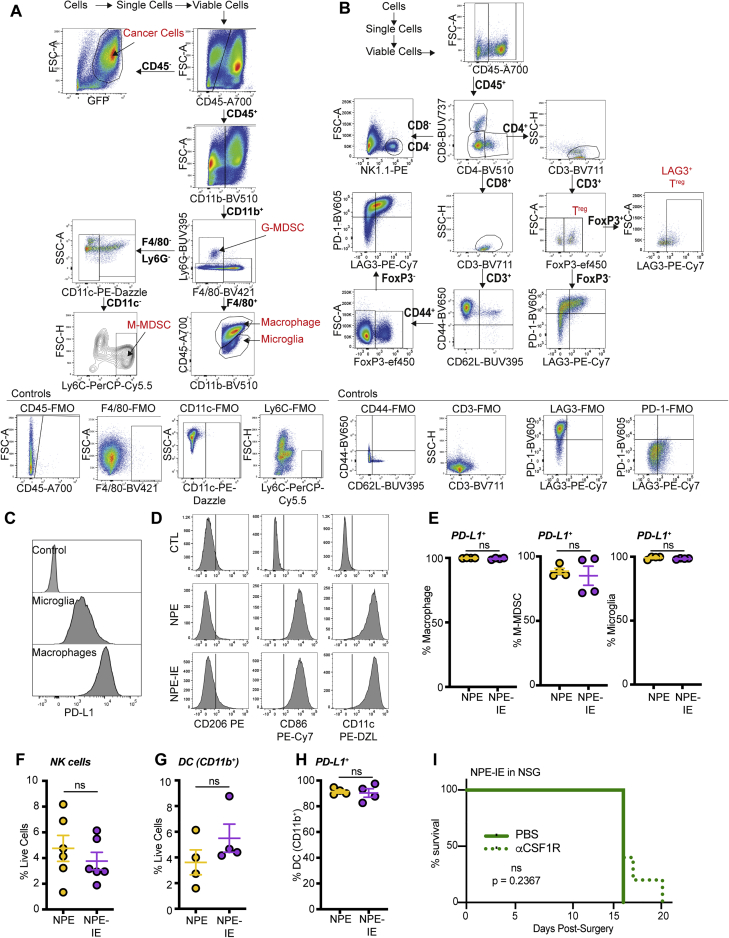
Figure S3.
Immune evasive NPE-IE tumors possess a highly immunosuppressive TME, related to Figure 3
(A) & (B) Gating strategy to define myeloid (A) and lymphoid (B) populations in NPE and NPE-IE tumors.
(C) Representative histograms of PD-L1 expression on microglia and macrophages in NPE-IE tumors (linked to Figure 3E). Control represents fully stained sample minus anti-PD-L1 antibody.
(D) Representative histograms of CD206, CD86 and CD11c expression on macrophages from NPE and NPE-IE tumors. Data derived from 3 tumors randomly down sampled for 50,000 live cells each. Control represents fully stained sample minus either anti-CD206, anti-CD86 or anti-CD11c antibodies.
(E) Flow cytometry quantification of the frequency of macrophages, M-MDSC and microglia positive for expression of PD-L1
(F) Flow cytometry quantification of the frequency of NK cells as a percentage of live cells.
(G) Flow cytometry quantification of the frequency of CD11b+ DCs as a percentage of live cells.
(H) Flow cytometry quantification of CD11b+ DCs positive for expression of PD-L1.
(I) Survival analysis of NSG mice orthotopically injected with NPE-IE cells subjected to IP injection of aCSF-1R or PBS (n = 5 mice + ɑCSF-1R; n = 3 mice +PBS; p = 0.2367).