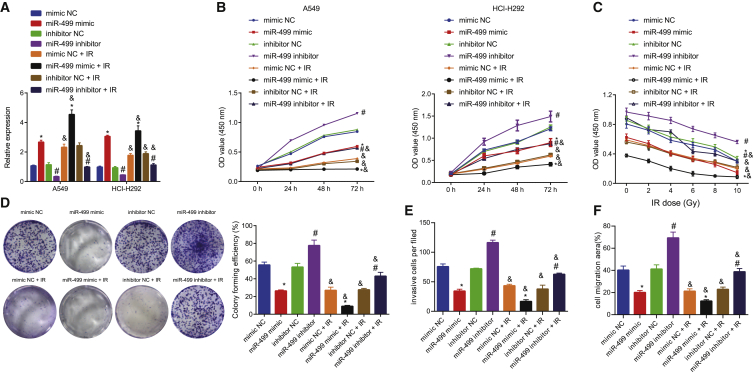
Figure 2.
Overexpression of miR-499 elevated the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to IR exposure
(A) The effectiveness of overexpression or inhibition of miR-499 determined by qRT-PCR. (B) The effect of overexpressed or suppressed miR-499 expression on cell viability determined by MTT assay (A549 and NCI-H292 cells). (C) The sensitivity of lung cancer A549 cells with overexpressed or suppressed miR-499 expression to irradiation (IR) determined by MTT assay. (D) The number of colonies of lung cancer A549 cells with overexpressed or suppressed miR-499 expression by colony-formation assay. (E) Cell invasion assay was performed to detect differences in invasion ability of A549 lung cancer cells treated with miR-499 mimic or miR-499 inhibitor. (F) Cell scratch assay was performed to detect differences in migration ability of A549 lung cancer cells treated with miR-499 mimic or miR-499 inhibitor. ∗p < 0.05 versus cells treated with mimic NC; #p < 0.05 versus cells treated with inhibitor NC, n = 3; &p < 0.05 versus the corresponding non-irradiated groups, n = 3. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Data between the two groups were compared using independent sample t test. Comparisons among multiple groups were conducted by ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. Statistical analysis in relation to different concentrations within each group was analyzed using two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. The experiments were repeated three times, with the representative result presented.